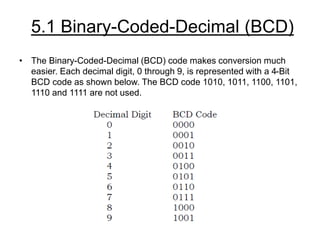
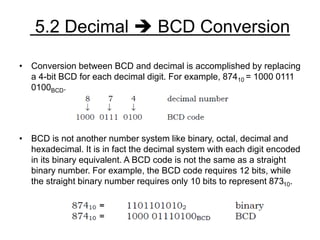
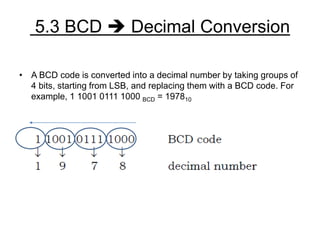
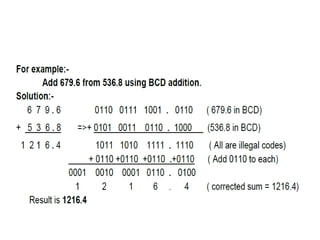
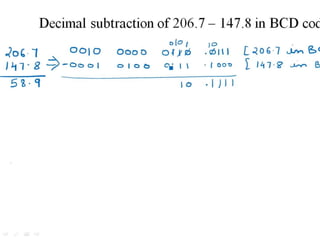
The document discusses 1's and 2's complement in the binary number system, explaining how to calculate them with given binary examples. It then introduces binary-coded decimal (BCD) as a method to simplify conversions between decimal and binary, detailing the representation of each decimal digit with a 4-bit BCD code. Additionally, it covers BCD addition and subtraction techniques, outlining corrections needed for invalid codes or borrowing during operations.