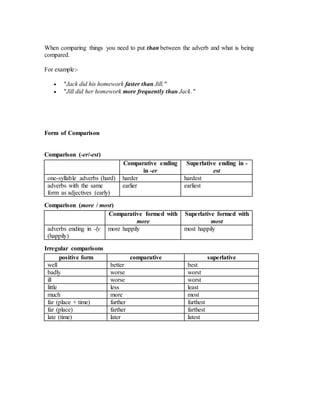
This document discusses the comparison of adverbs in English. It explains that adverbs have three degrees of comparison: positive, comparative, and superlative. Adverbs ending in -ly form the comparative with "more" and the superlative with "most". One-syllable adverbs and adverbs that are also adjectives form the comparative with "-er" and the superlative with "-est". Some common adverbs like "well", "badly", and "little" have irregular comparative and superlative forms. The document provides examples of forming the three degrees of comparison for different types of adverbs and exercises for practice.