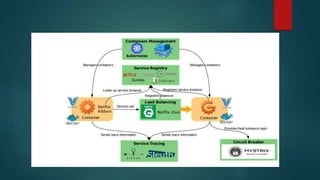
The document discusses microservices architecture, highlighting its advantages such as modular systems, targeted scaling, agility, and high availability. It addresses the concerns associated with implementing microservices, including containerization, service discovery, load balancing, service tracing, circuit breakers, and maintaining consistency through service templates. Netflix is cited as an example of a successful adopter of microservices architecture.