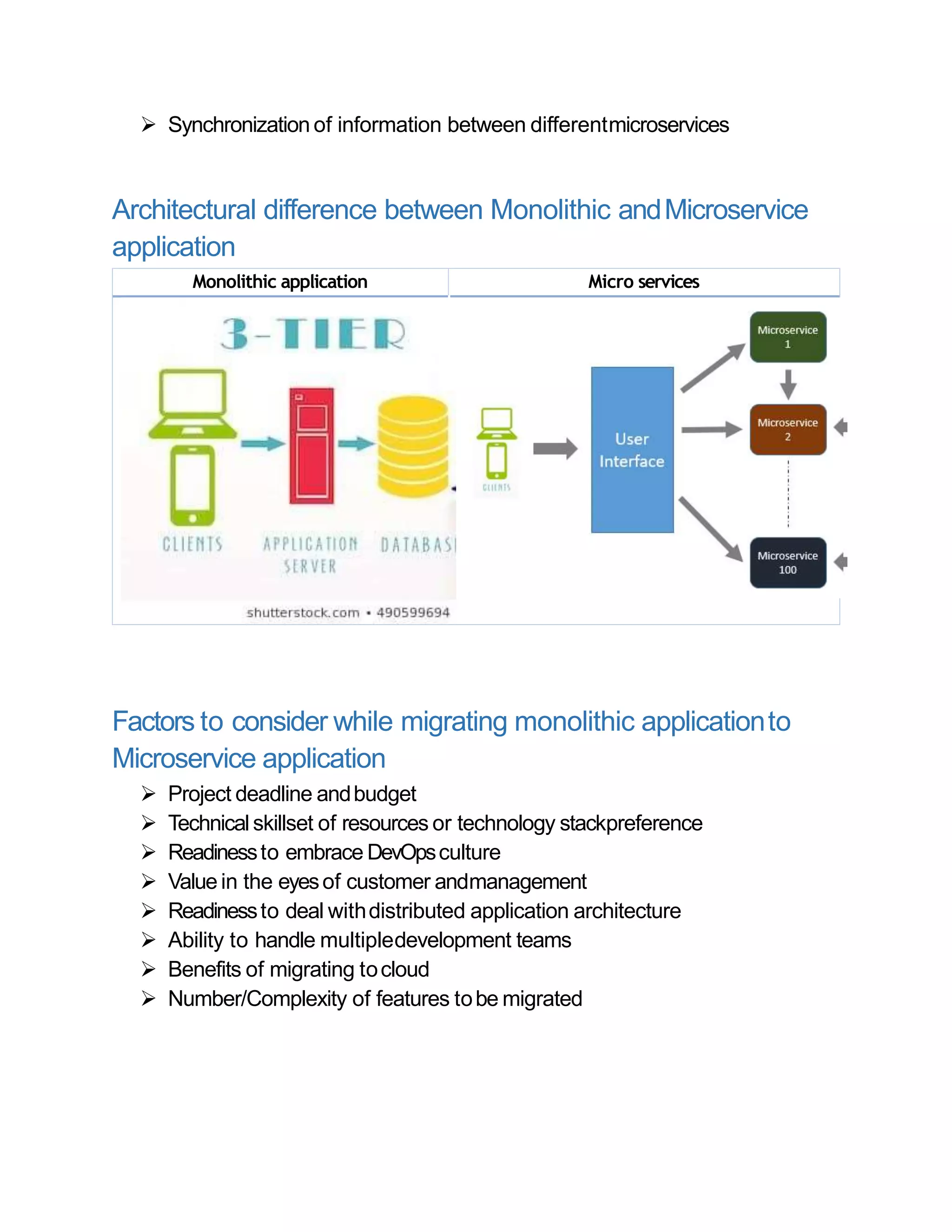
The document explains the transition from monolithic applications to microservices, highlighting the advantages of microservices such as scalability, independent deployment, and suitability for cloud environments. It contrasts the characteristics and challenges of both architectures, emphasizing the difficulties associated with monolithic systems like troubleshooting and scalability. Additionally, it outlines considerations for organizations planning to migrate, including team readiness, technical skillsets, and project management factors.