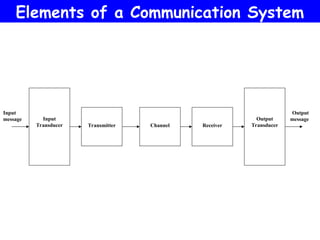
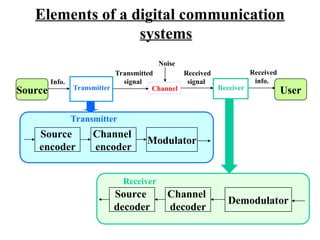
The document outlines the evolution of communication systems from early inventions like the telegraph and telephone to modern digital and satellite technologies. It describes key components of communication systems, including input and output transducers, transmitters, channels, and receivers, as well as the significance of modulation. Additionally, it highlights major milestones in the field from 1800 to 2050, indicating the ongoing advancements in communication technology.