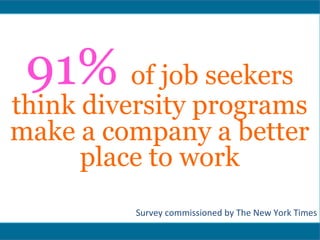
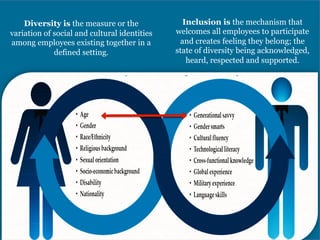
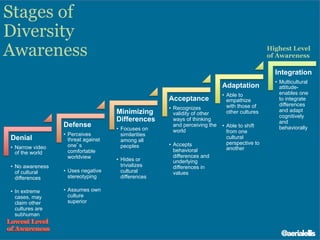
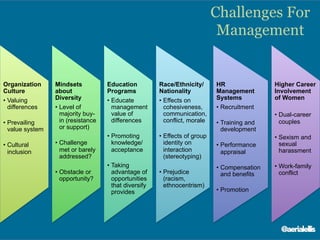
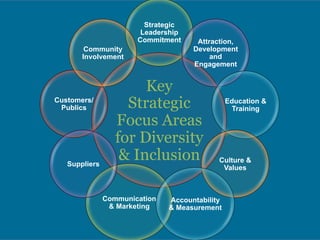
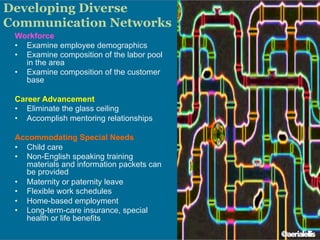
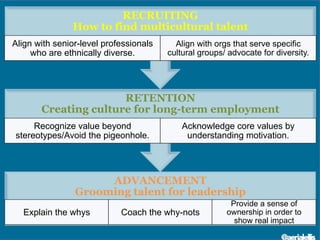
The document discusses significant demographic shifts, projected to see the senior population double by 2030 and millennials making up 75% of the U.S. workforce by 2025. It highlights the importance of workplace diversity and inclusion, arguing that organizations with diverse leadership experience higher returns on investment and innovation. Strategic imperatives are evolving, necessitating improved cultural competence, diverse hiring practices, and holistic approaches to HR and PR in fostering inclusive environments.














![LET’S CONNECT
Aerial Ellis
Strategist | Speaker | Trainer
[Communication, Culture,
Diversity, Change, Community]
Talk to Me:
615.307.0460
Book Me:
hello@aerialellis.com
Work with Me
LinkedIn: aerialellis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationcommunicatingthecasefordiversityandinclusiononline-161119043132/85/Communicating-the-Case-for-Diversity-and-Inclusion-22-320.jpg)