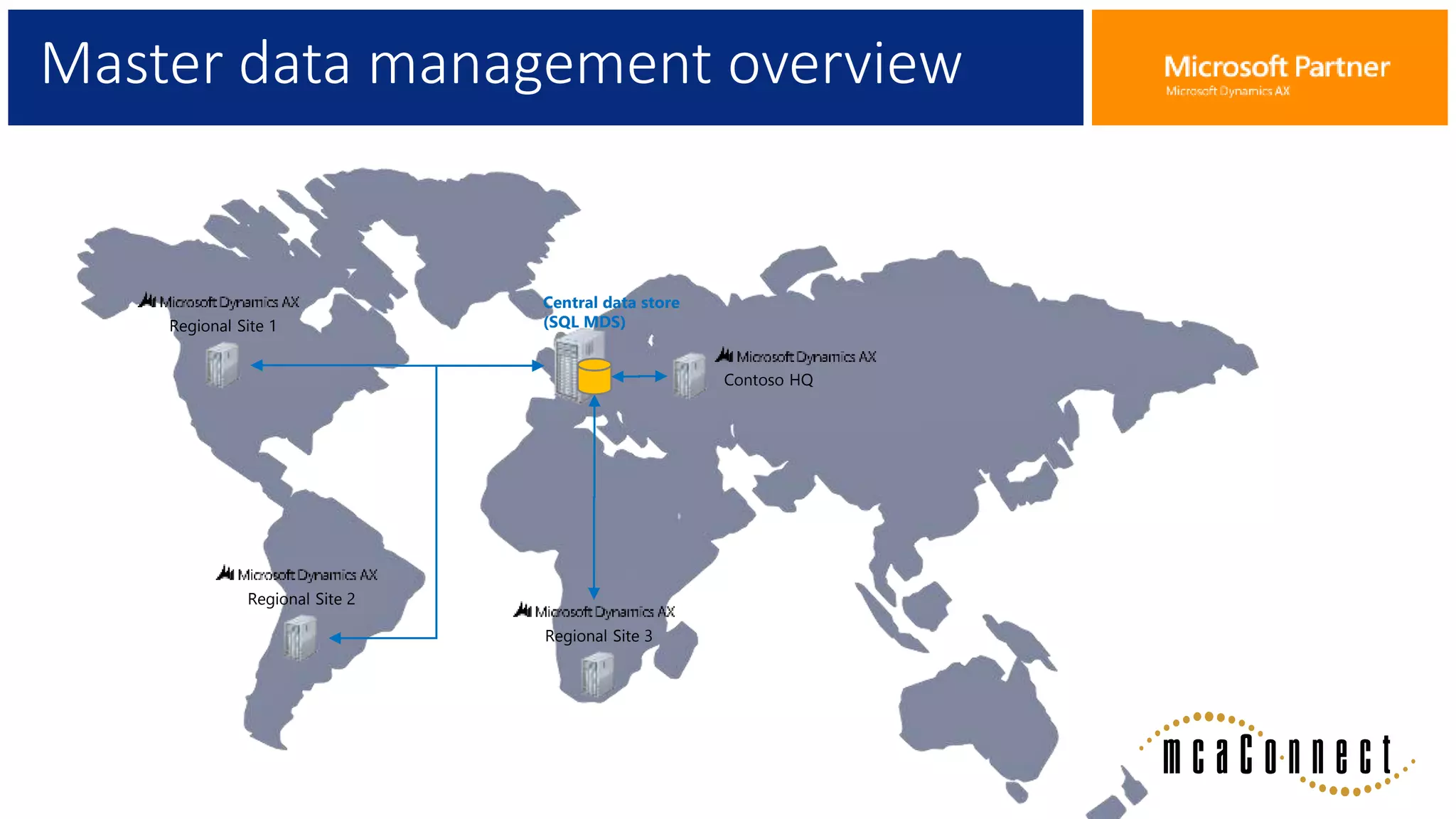
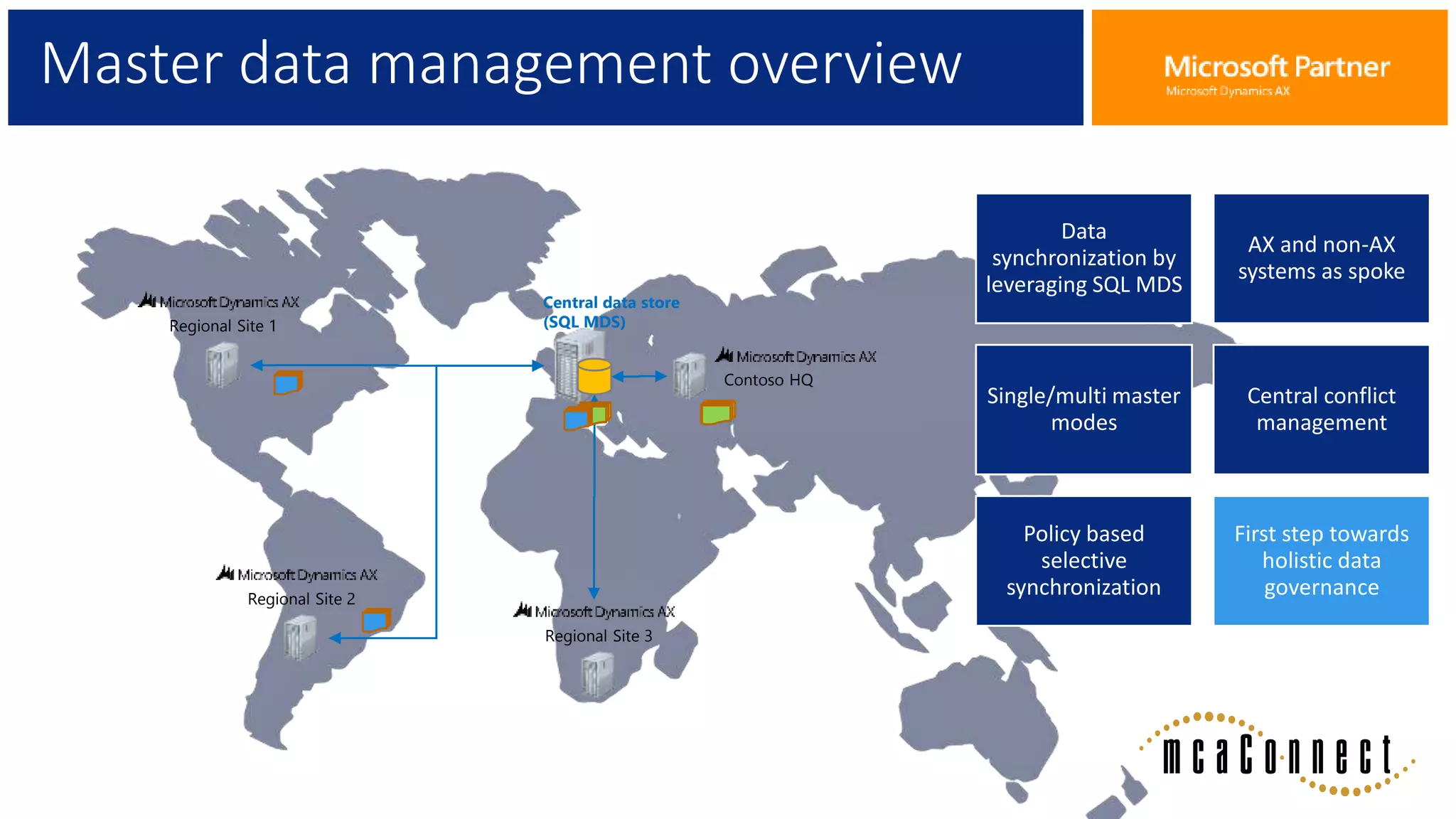
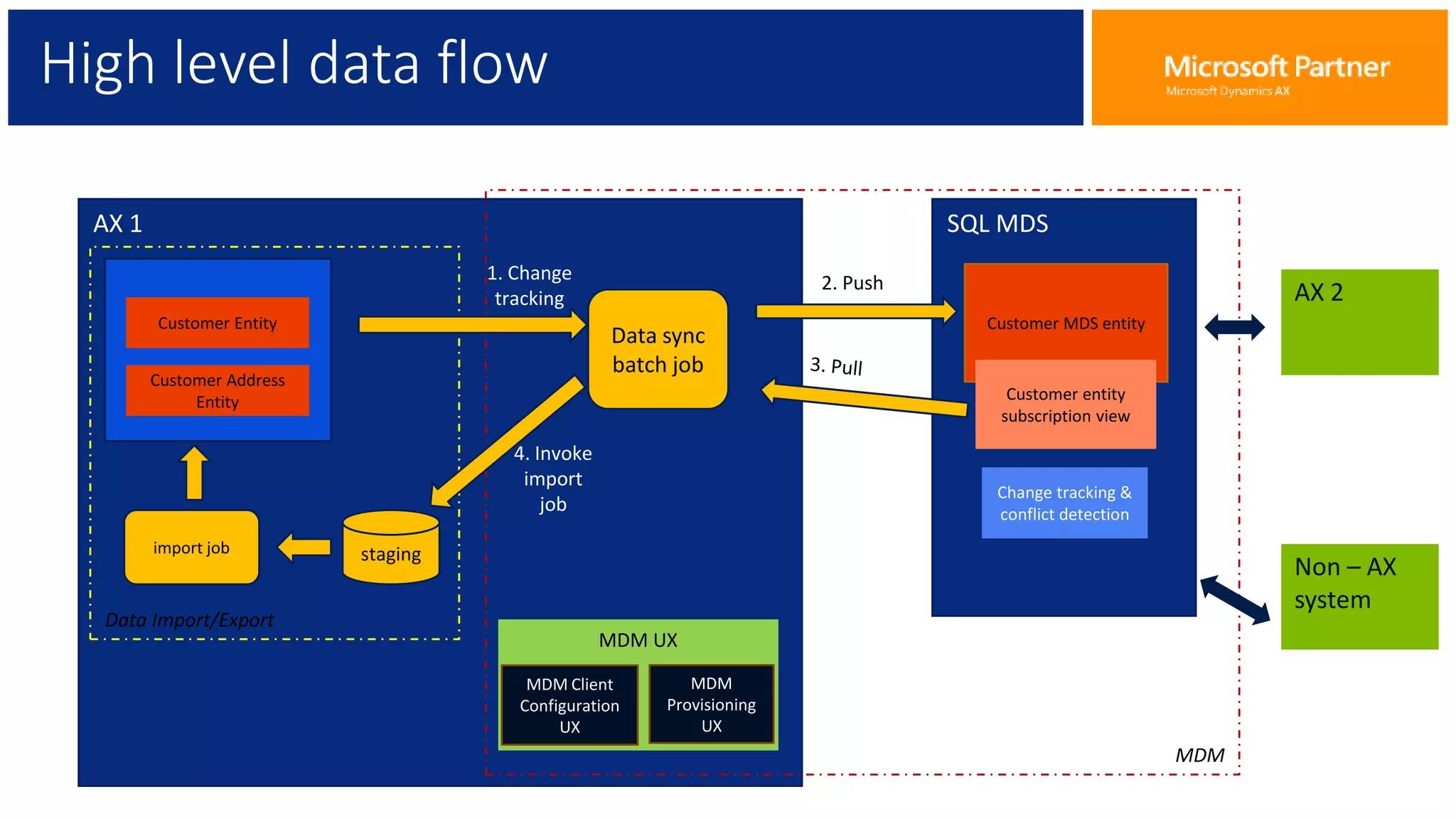
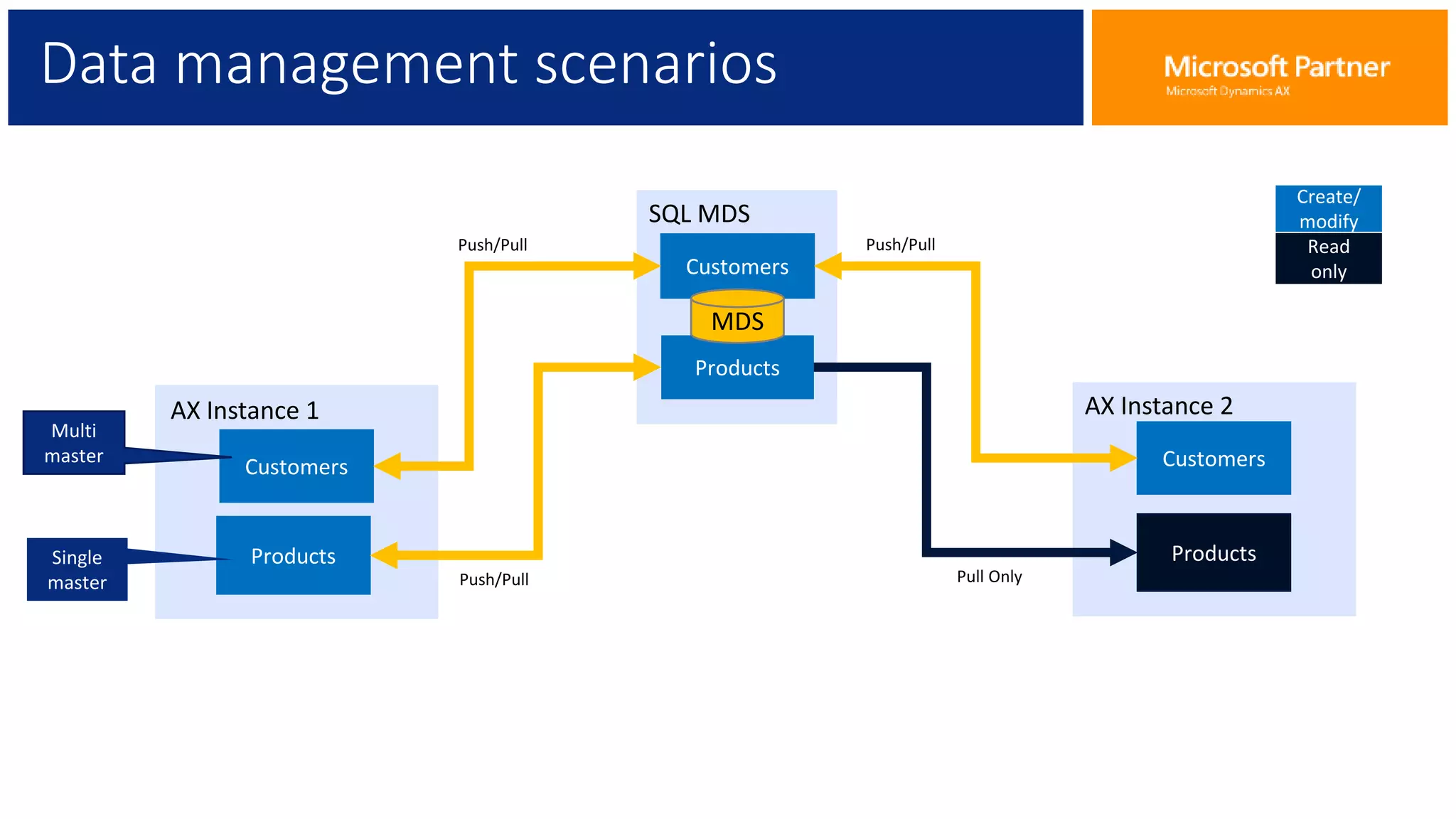
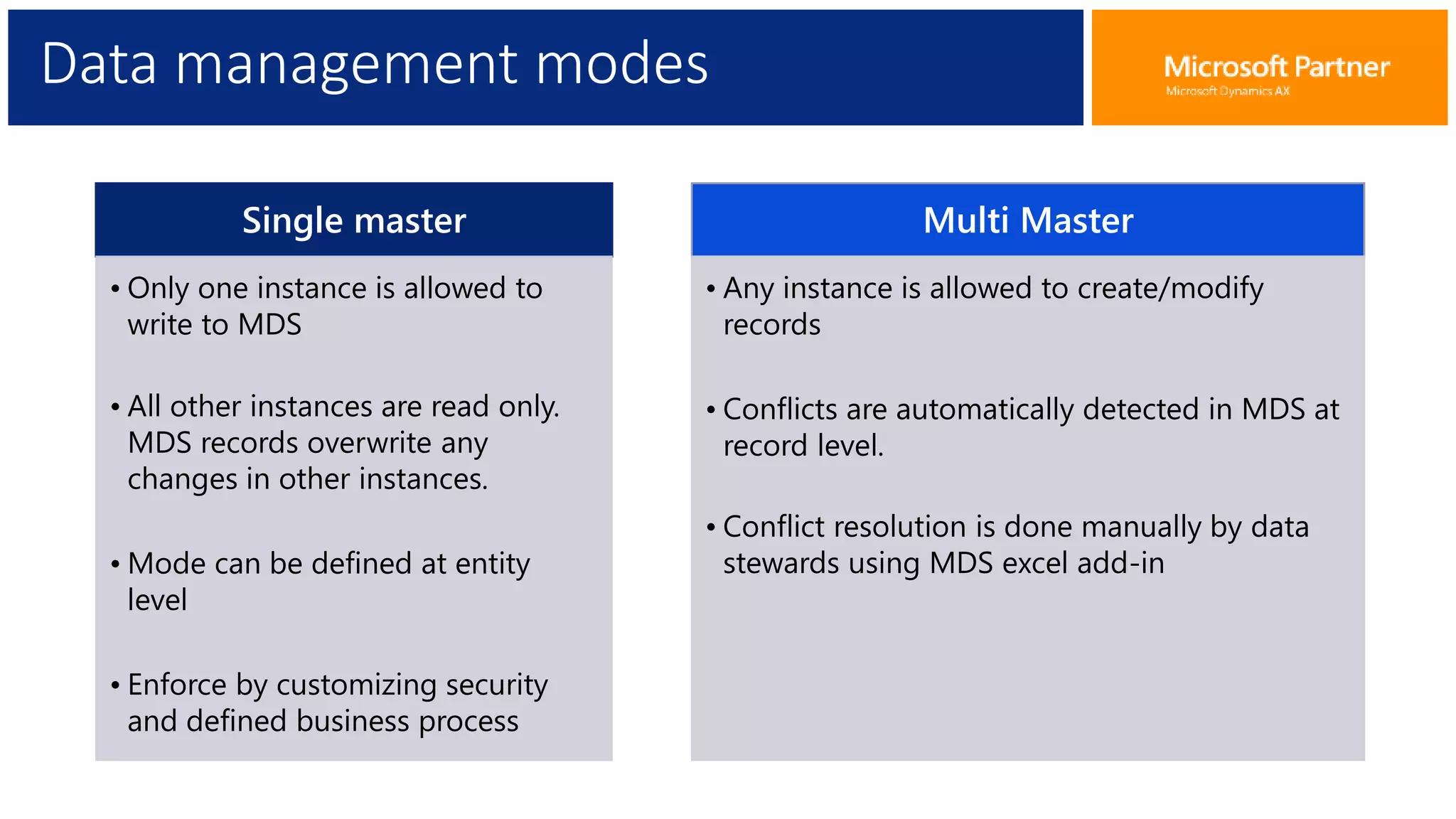
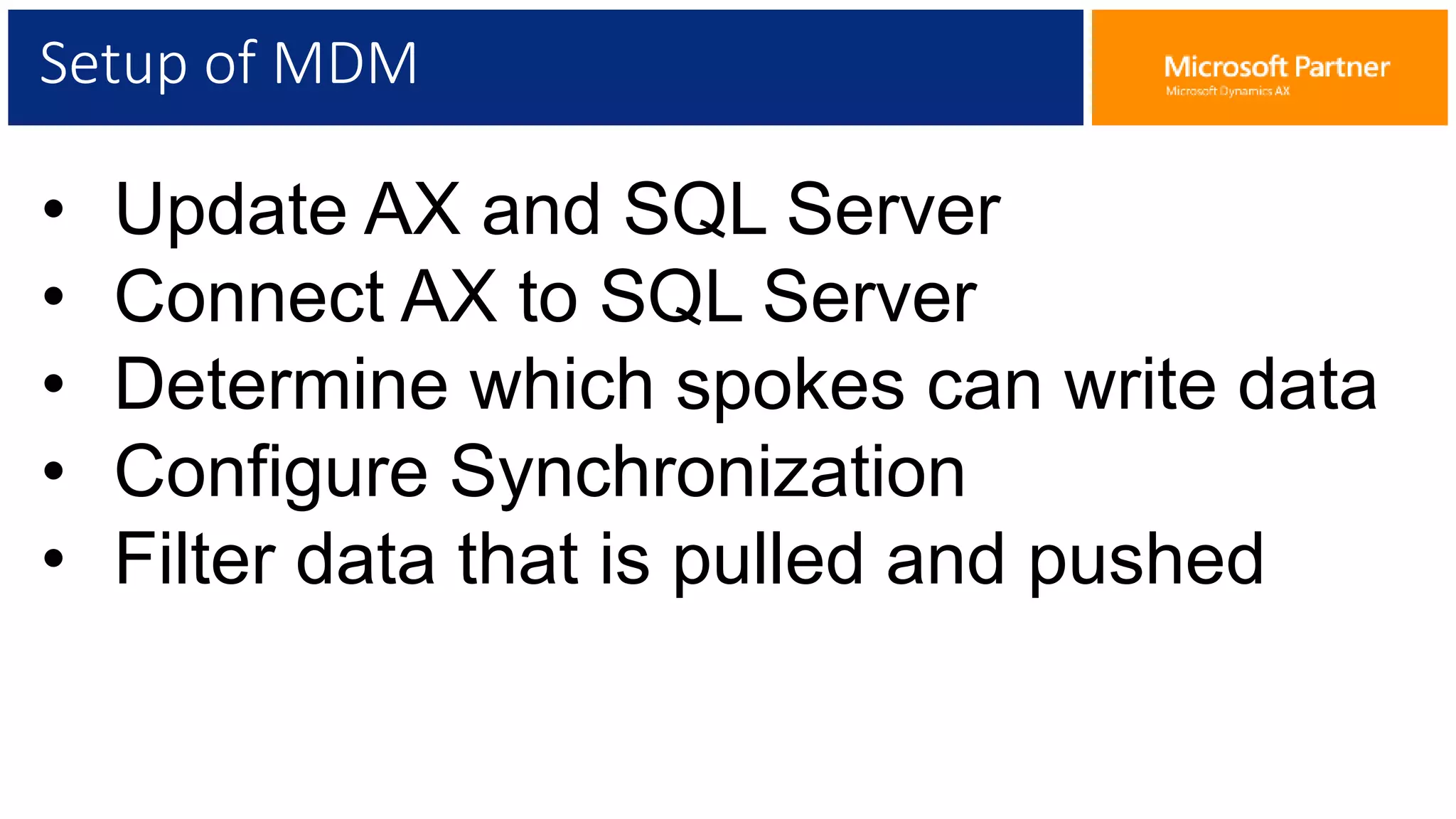
The document provides an overview of Master Data Management (MDM), including its definition, integration with AX, and setup procedures. MDM is described as a system that ensures a single source of truth for reference data across an enterprise, facilitating data synchronization and governance. The document also covers data import/export frameworks and management modes like single and multi-master configurations.