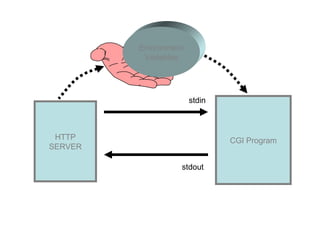
The Common Gateway Interface (CGI) allows web servers to interface with external applications. When a request is made for a CGI resource, the web server executes the associated program and returns the output. CGI programs can be written in many languages and access data passed in through environment variables or HTTP requests. Form data submitted via GET is appended to the URL, while POST submits data through standard input.