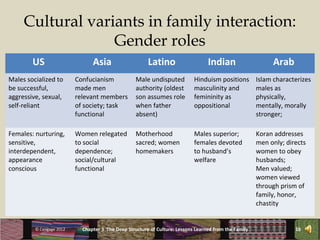
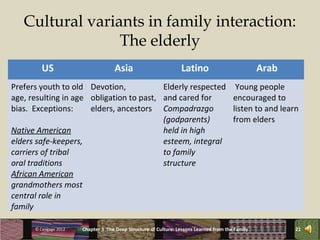
The chapter discusses how social institutions like the family shape a culture's deep structures. It explores how the family influences core cultural assumptions and how family structures vary across cultures. Key points covered include how the family socializes members, its role in cultural reproduction, and how concepts like individualism versus collectivism impact family dynamics in different societies. Gender roles and expectations for family interactions also vary significantly between cultures.