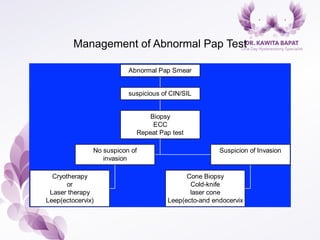
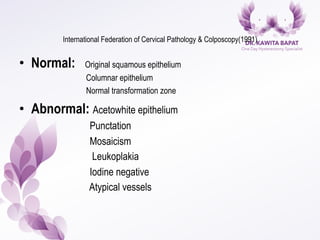
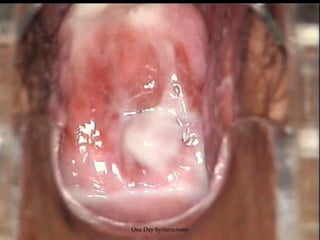
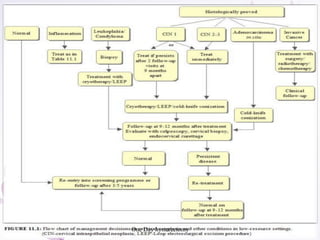
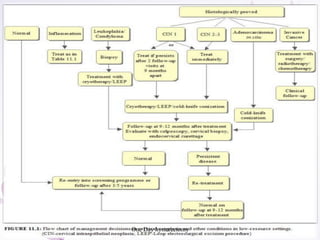
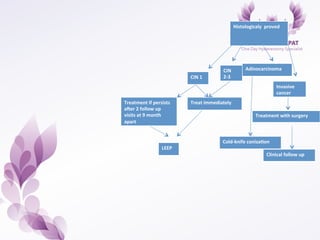
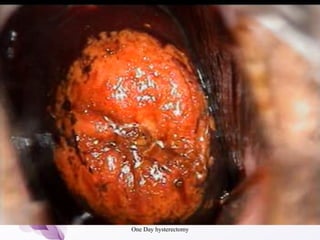
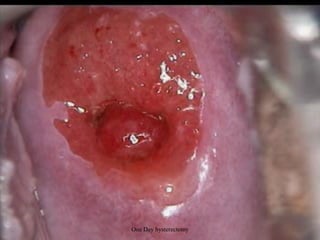
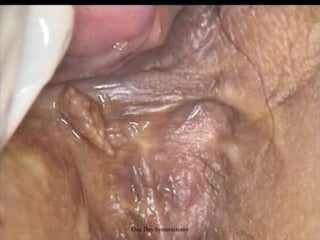
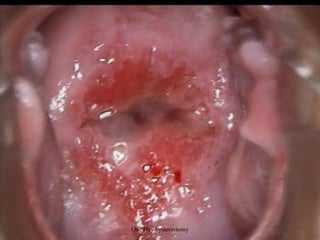
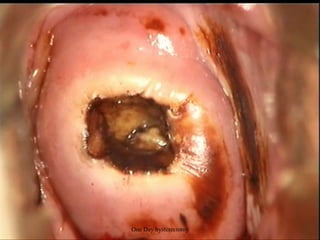
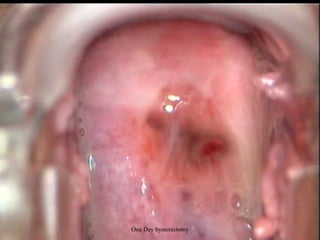
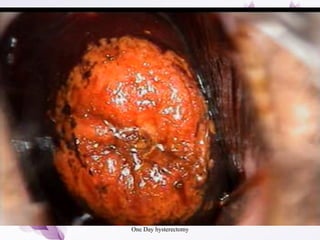
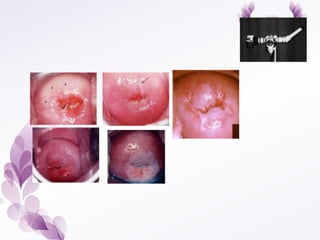
This document provides an overview of colposcopy techniques and procedures for diagnosing and treating cervical lesions. It discusses the use of colposcopy for examination of the cervix using magnification and acetic acid to identify abnormalities. Various treatment modalities are described including cryotherapy, laser therapy, LEEP, and cone biopsy. Guidelines are presented for managing low-grade versus high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. The document emphasizes the importance of accurate diagnosis and avoiding overtreatment. It concludes that a simplified approach can reduce costs while still effectively investigating and managing patients.