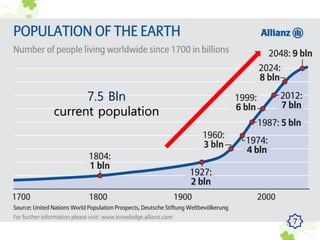
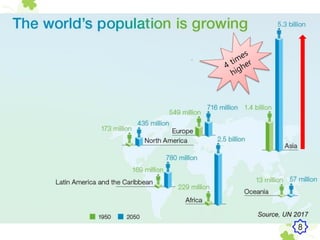
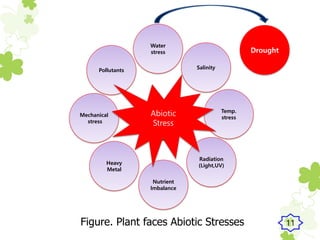
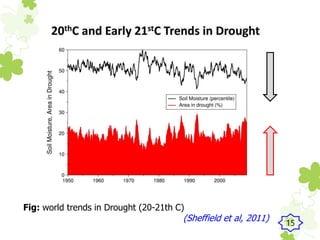
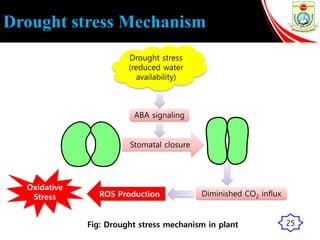
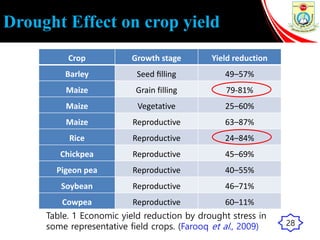
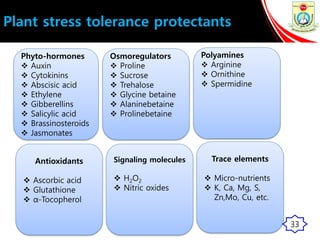
This presentation outlines the mechanisms of drought tolerance in plants. It discusses how drought stress affects crop growth and yield, and the various tolerance mechanisms plants have evolved, including escape, avoidance, and tolerance. Drought stress can cause oxidative stress in plants through increased reactive oxygen species production. Plants have developed morphological, physiological and biochemical modifications to cope with drought, such as osmotic adjustment, antioxidant production, and hormonal signaling. Integrating molecular approaches with conventional breeding is recommended to develop new crop varieties with improved drought resistance and ensure future food security.