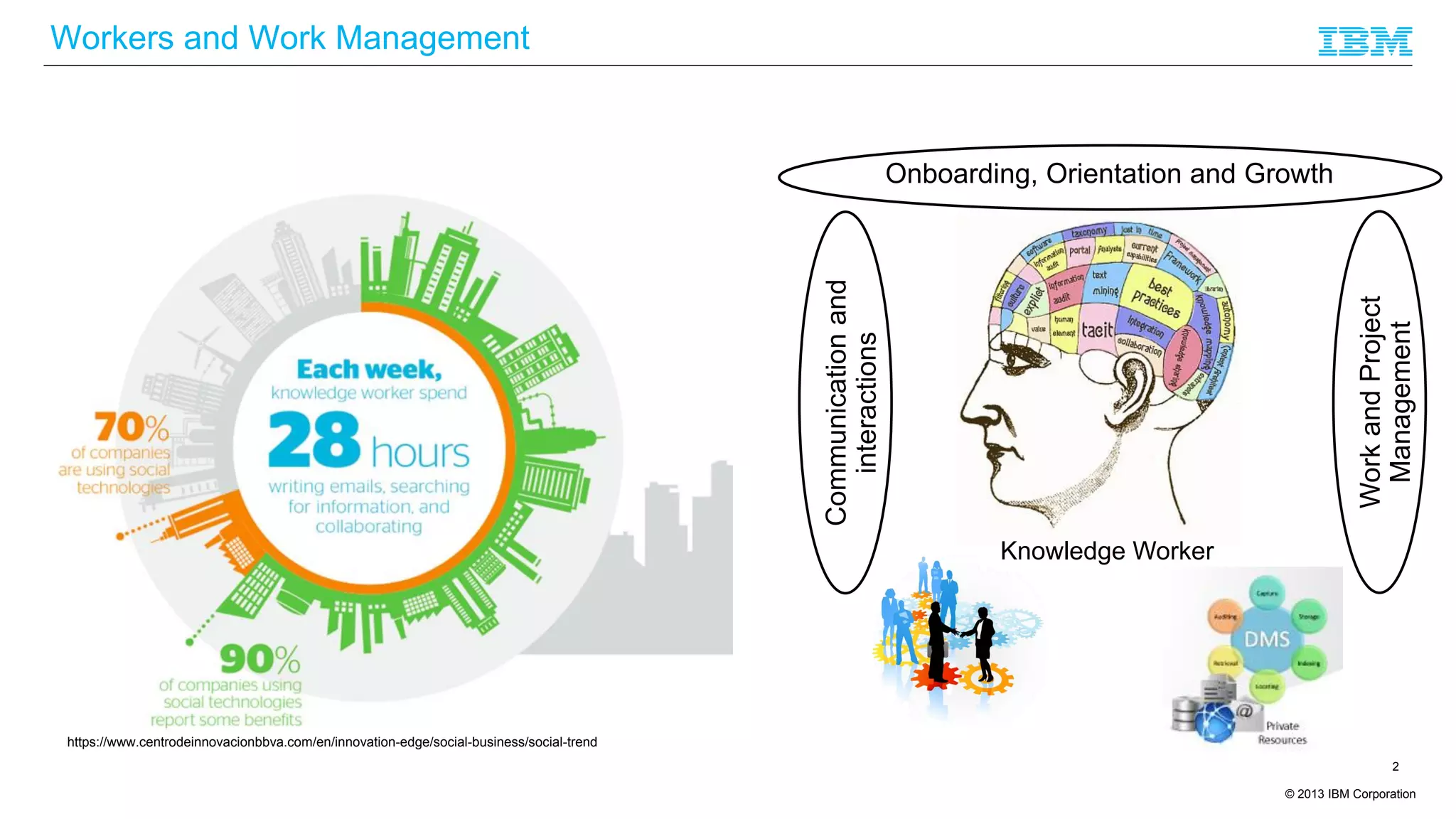
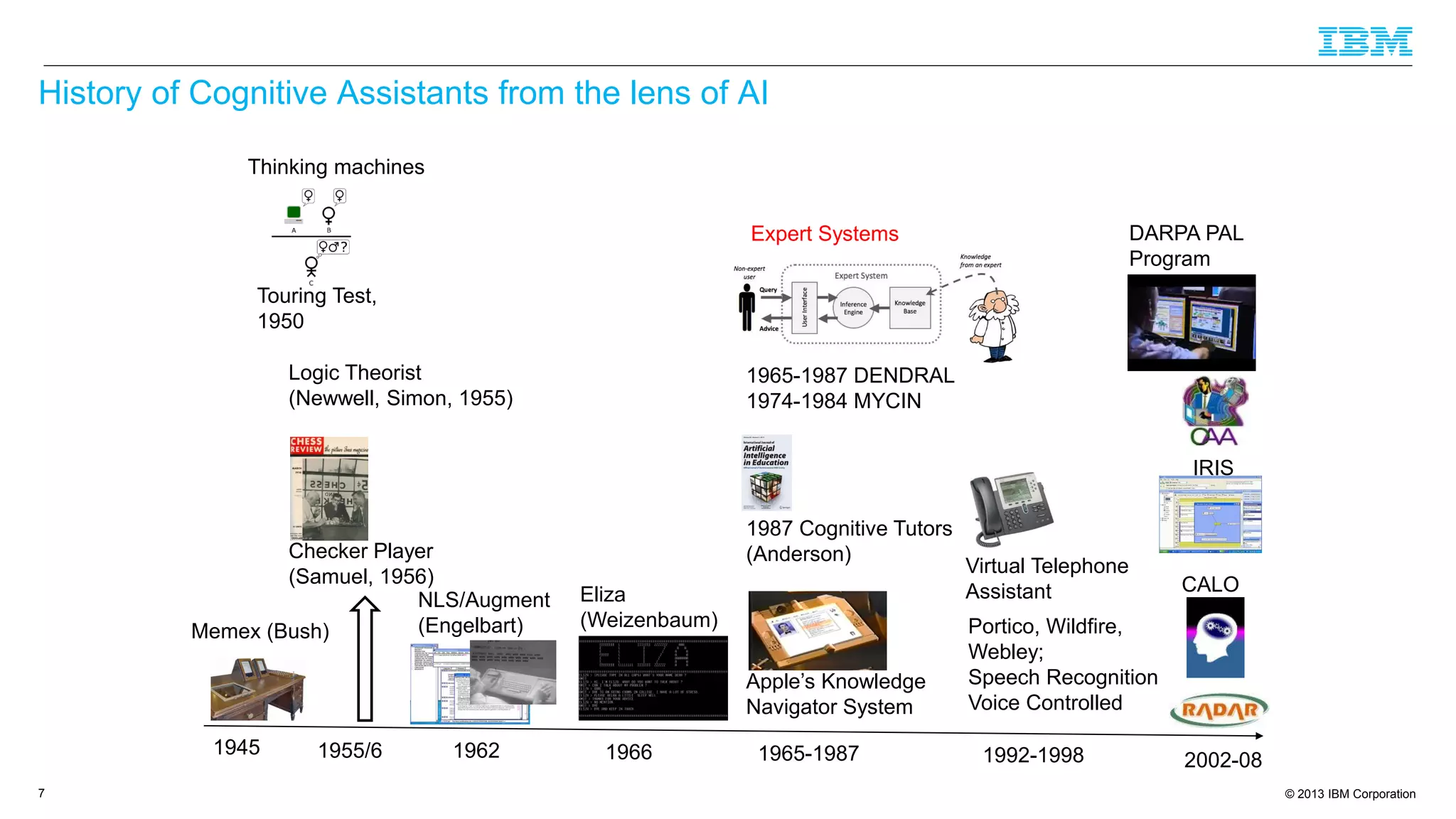
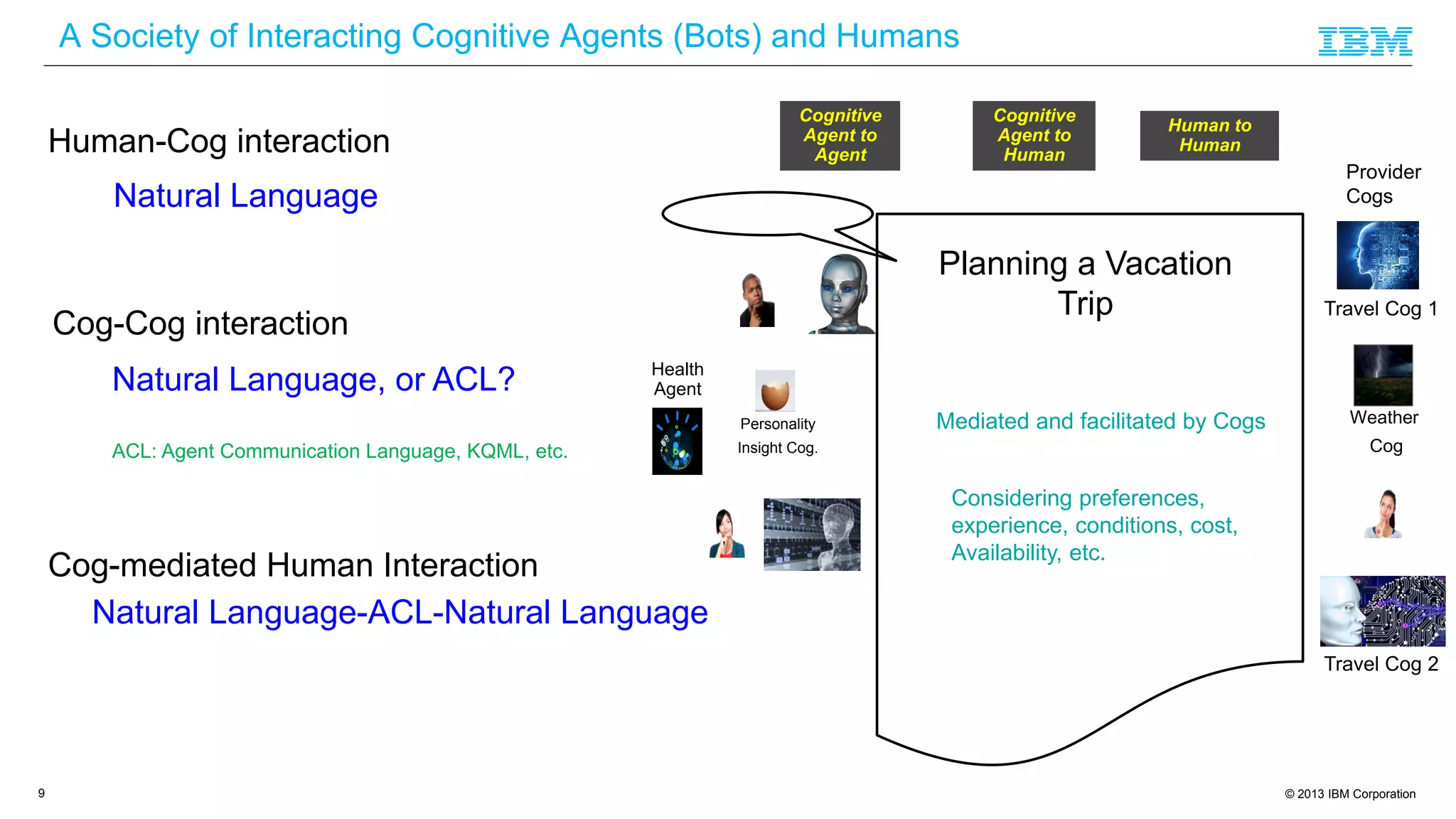
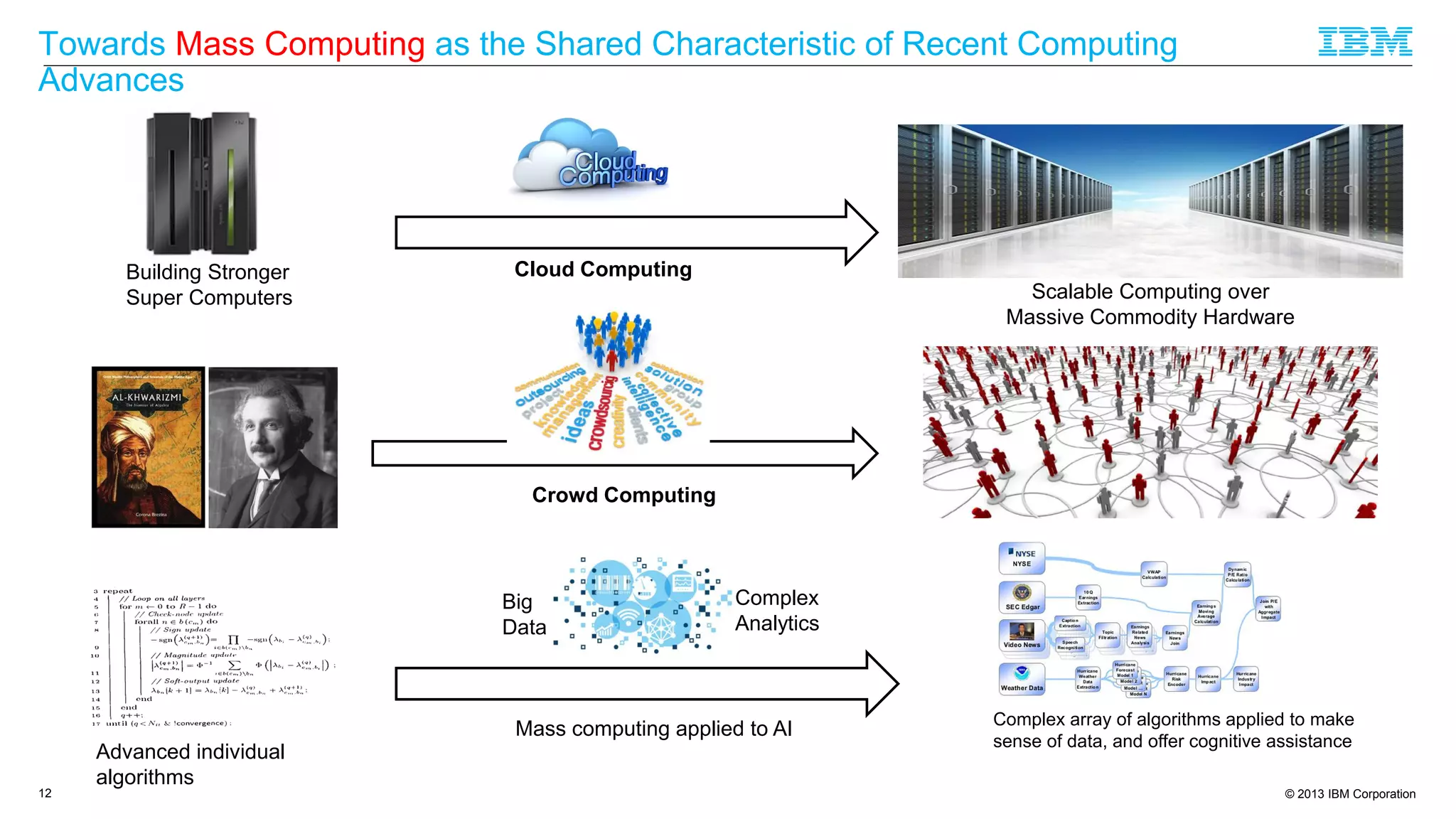
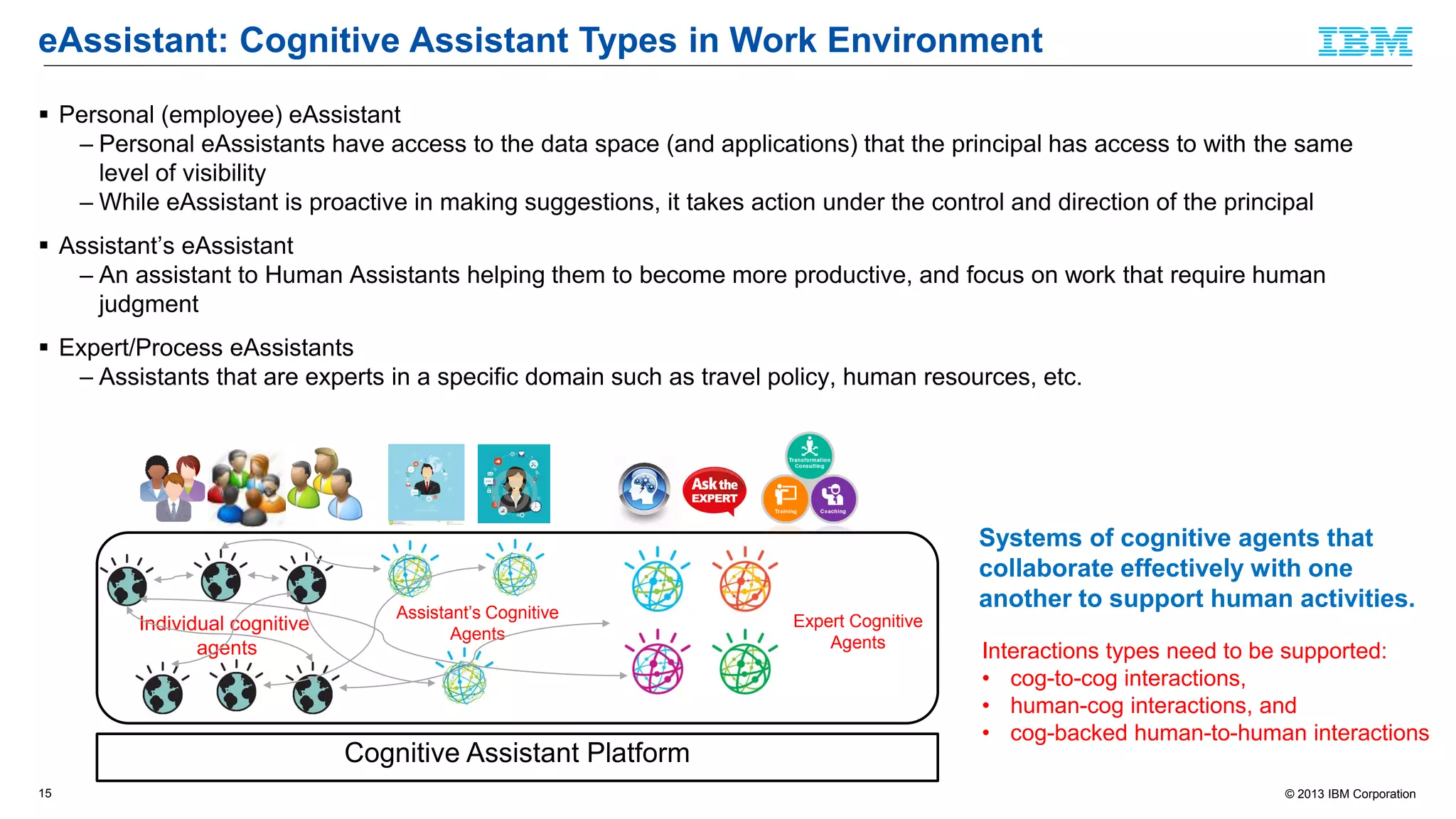
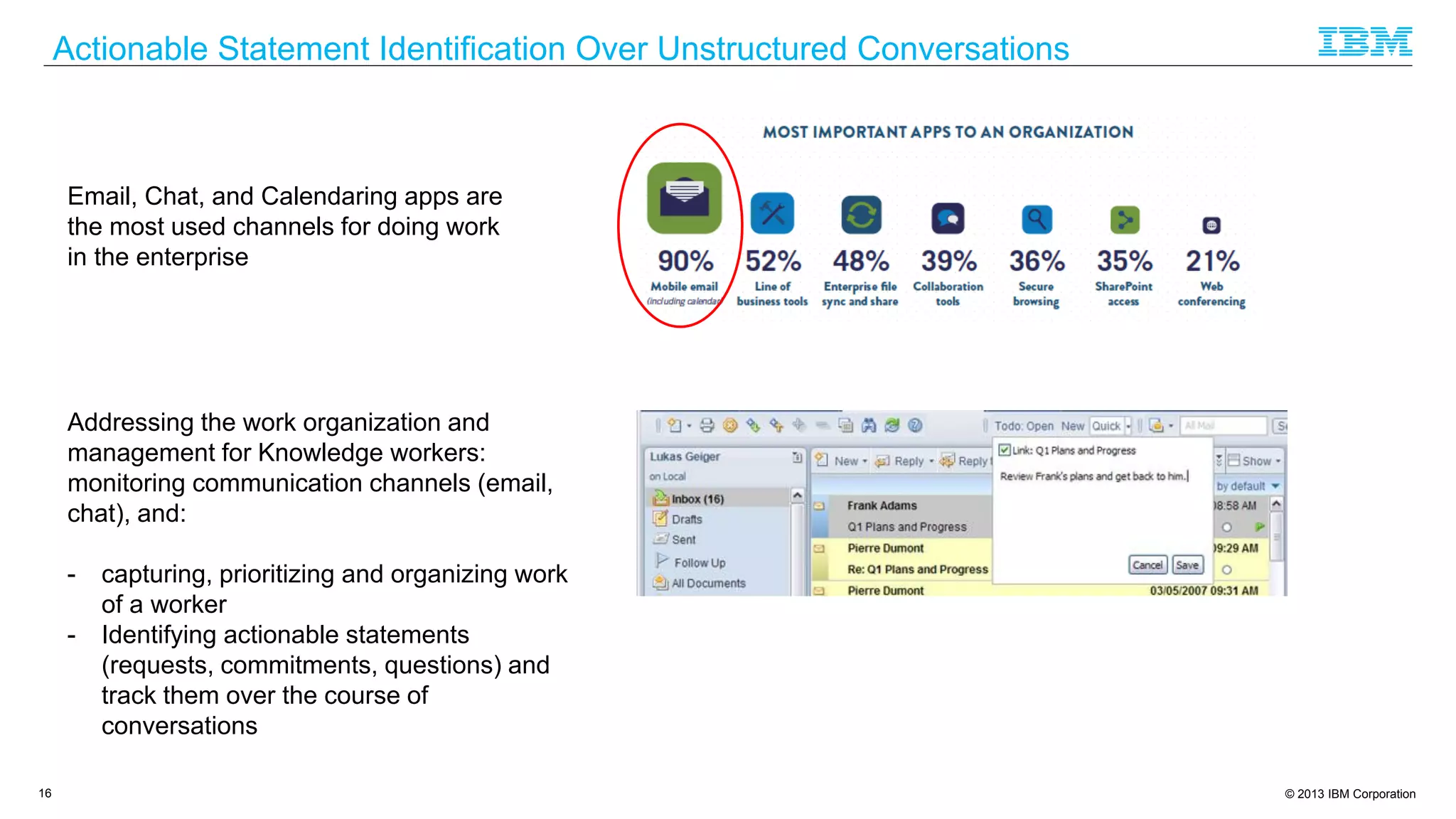
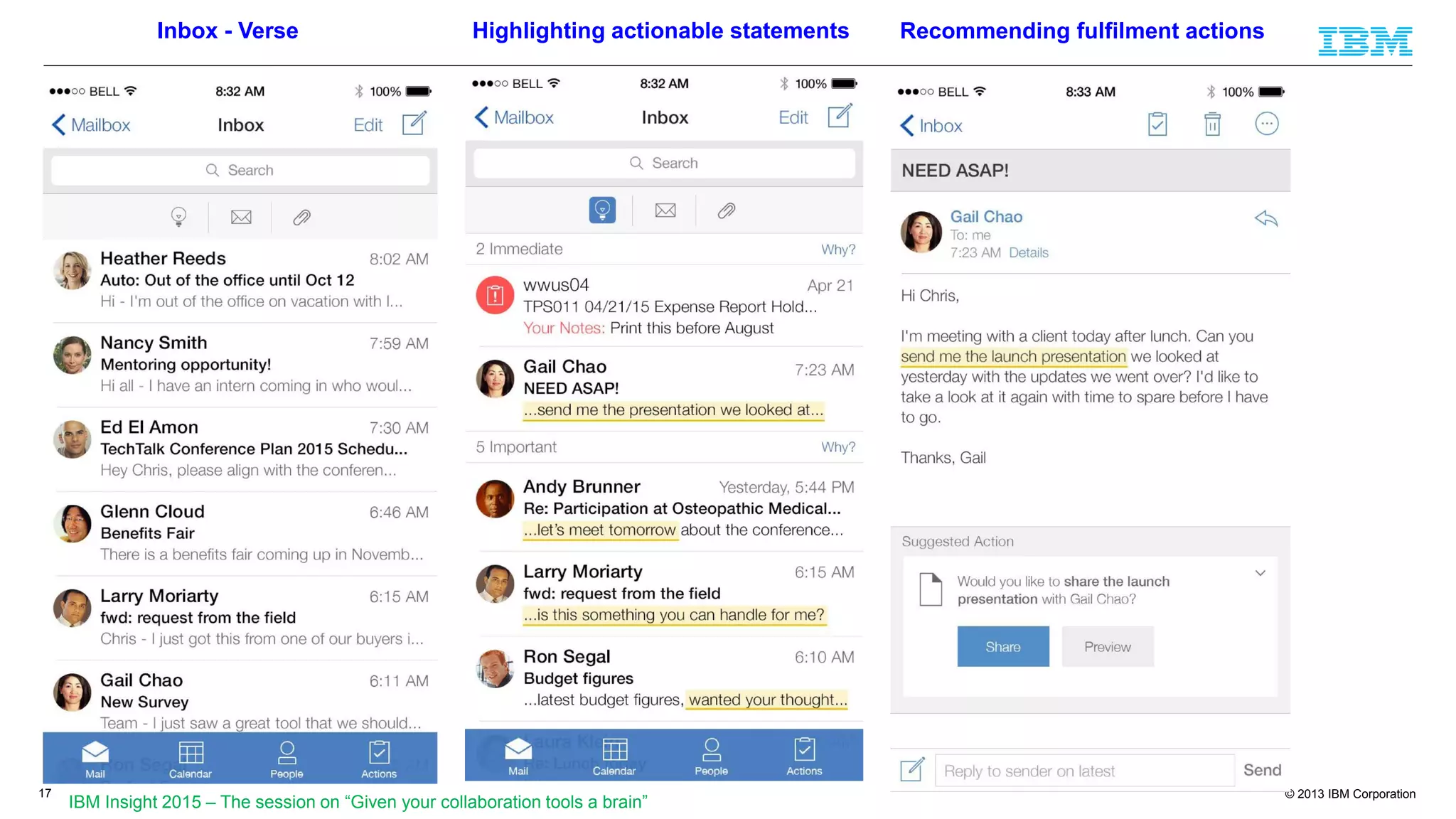
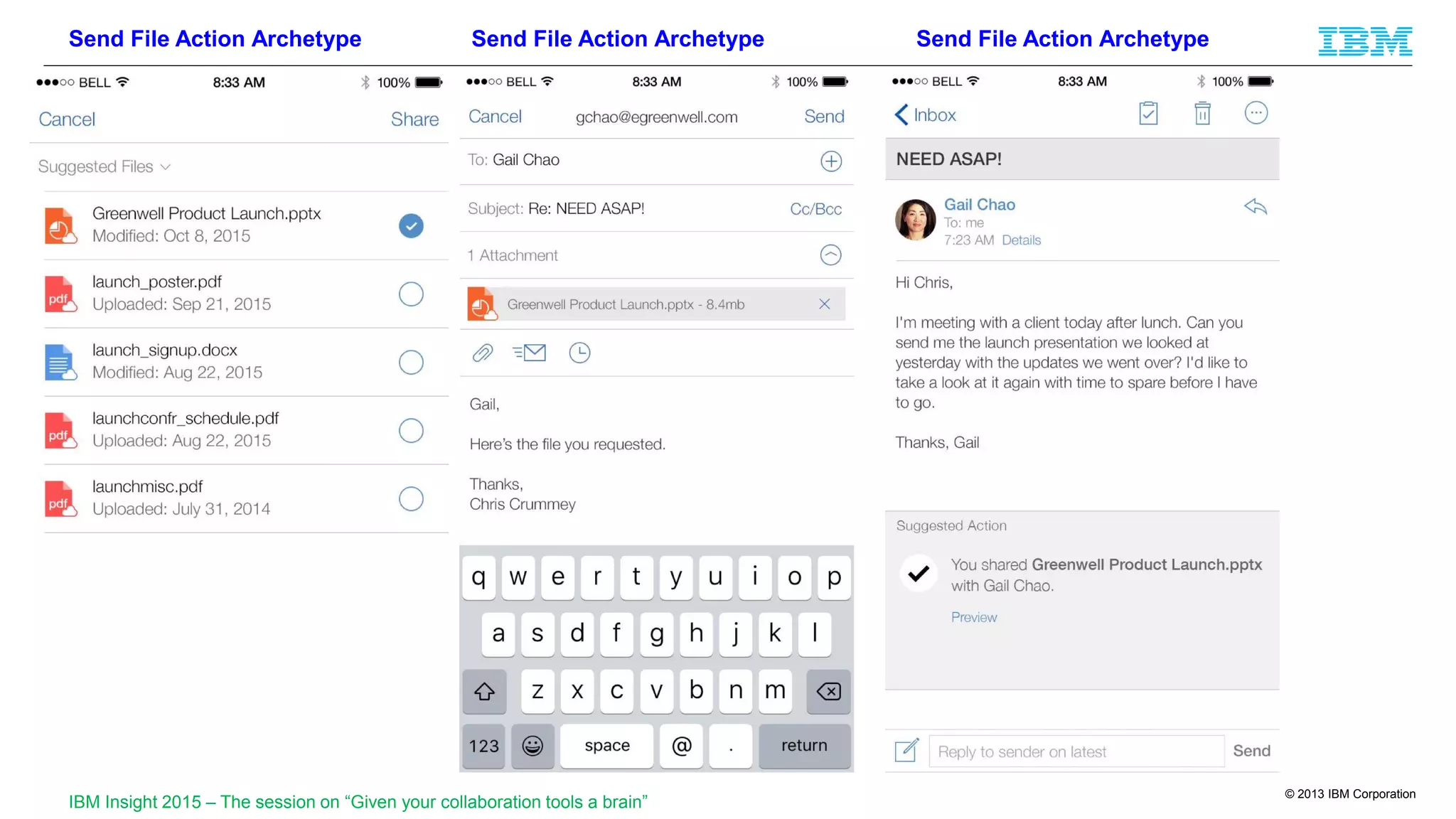
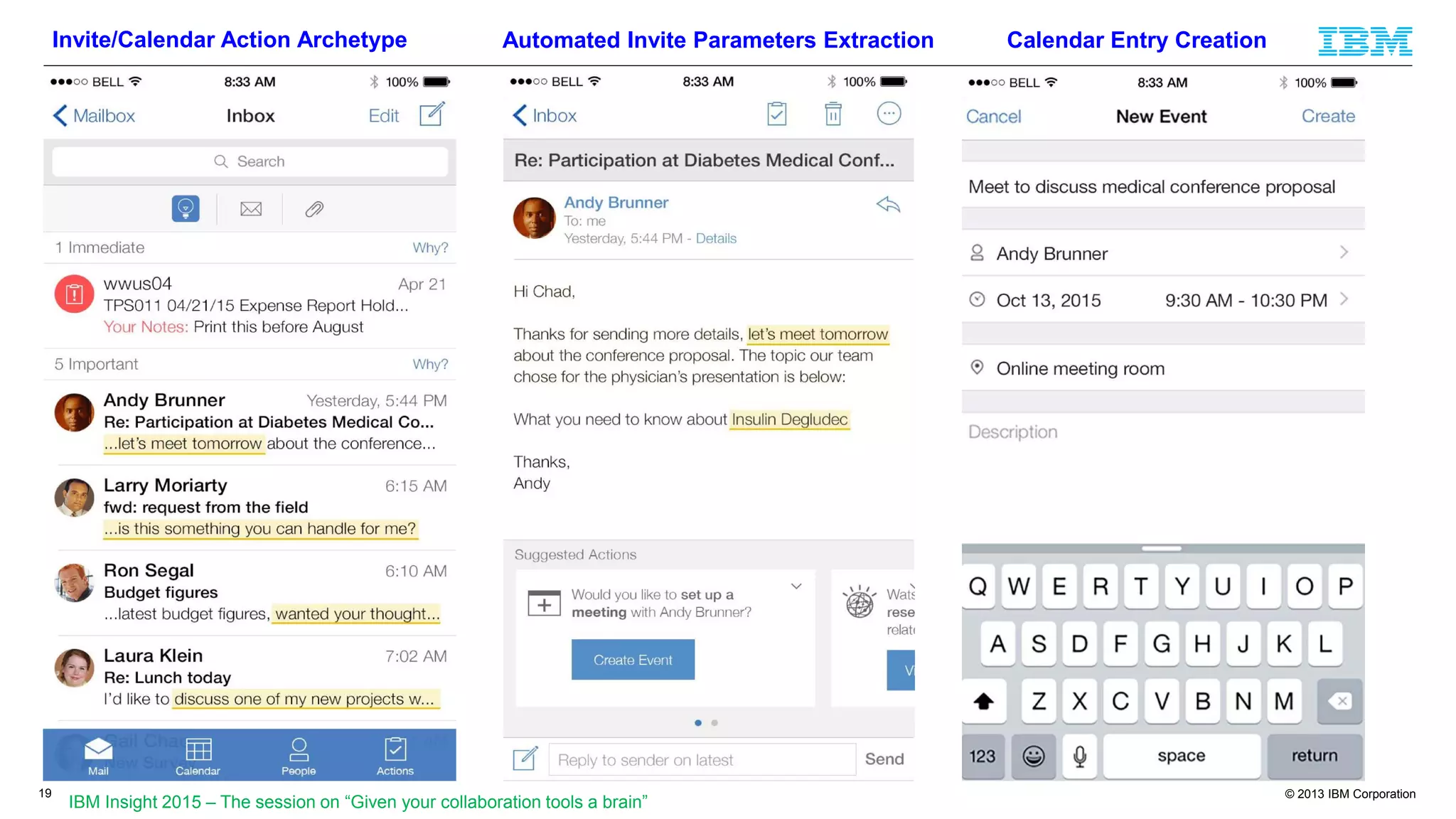
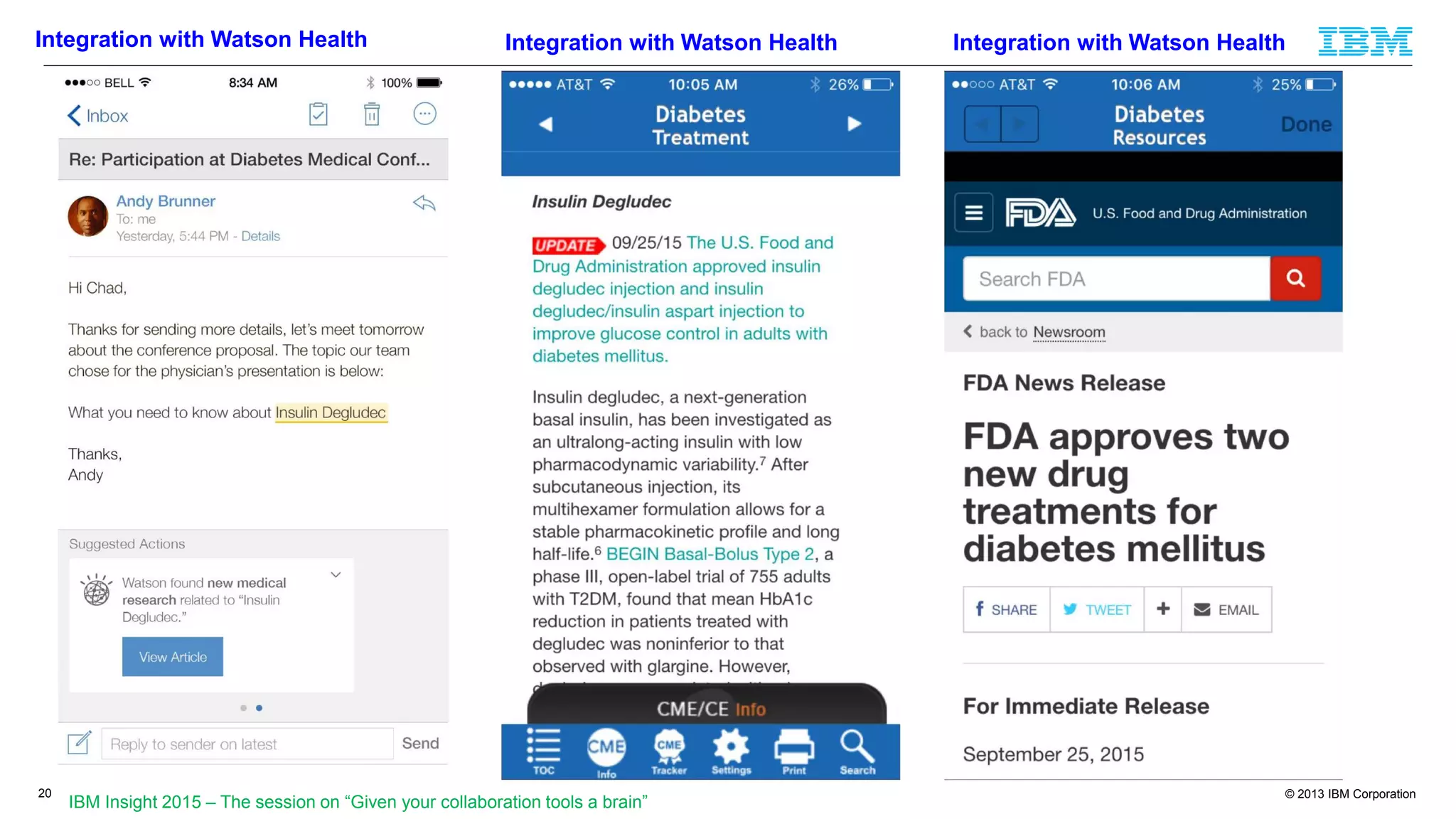
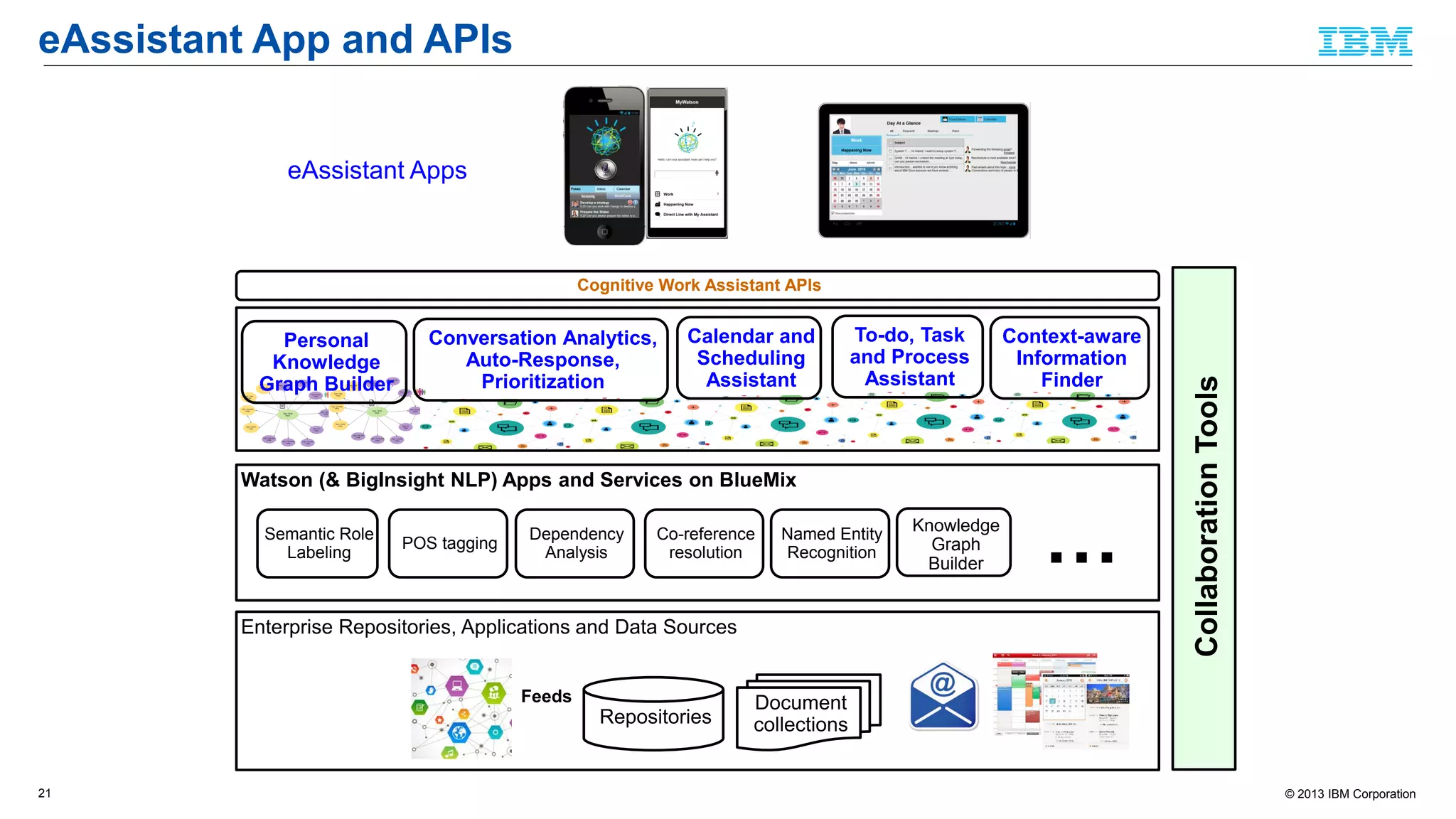
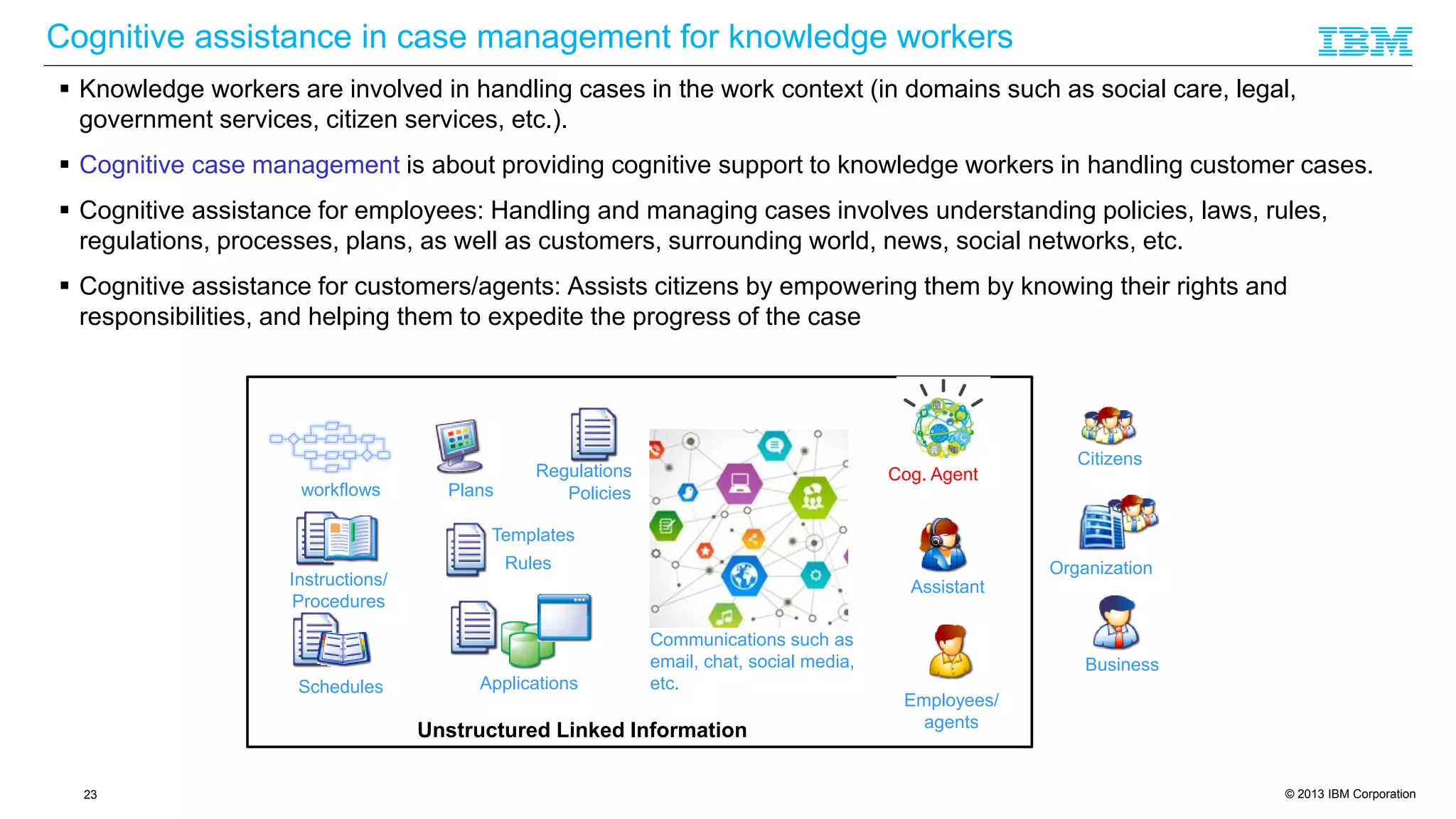
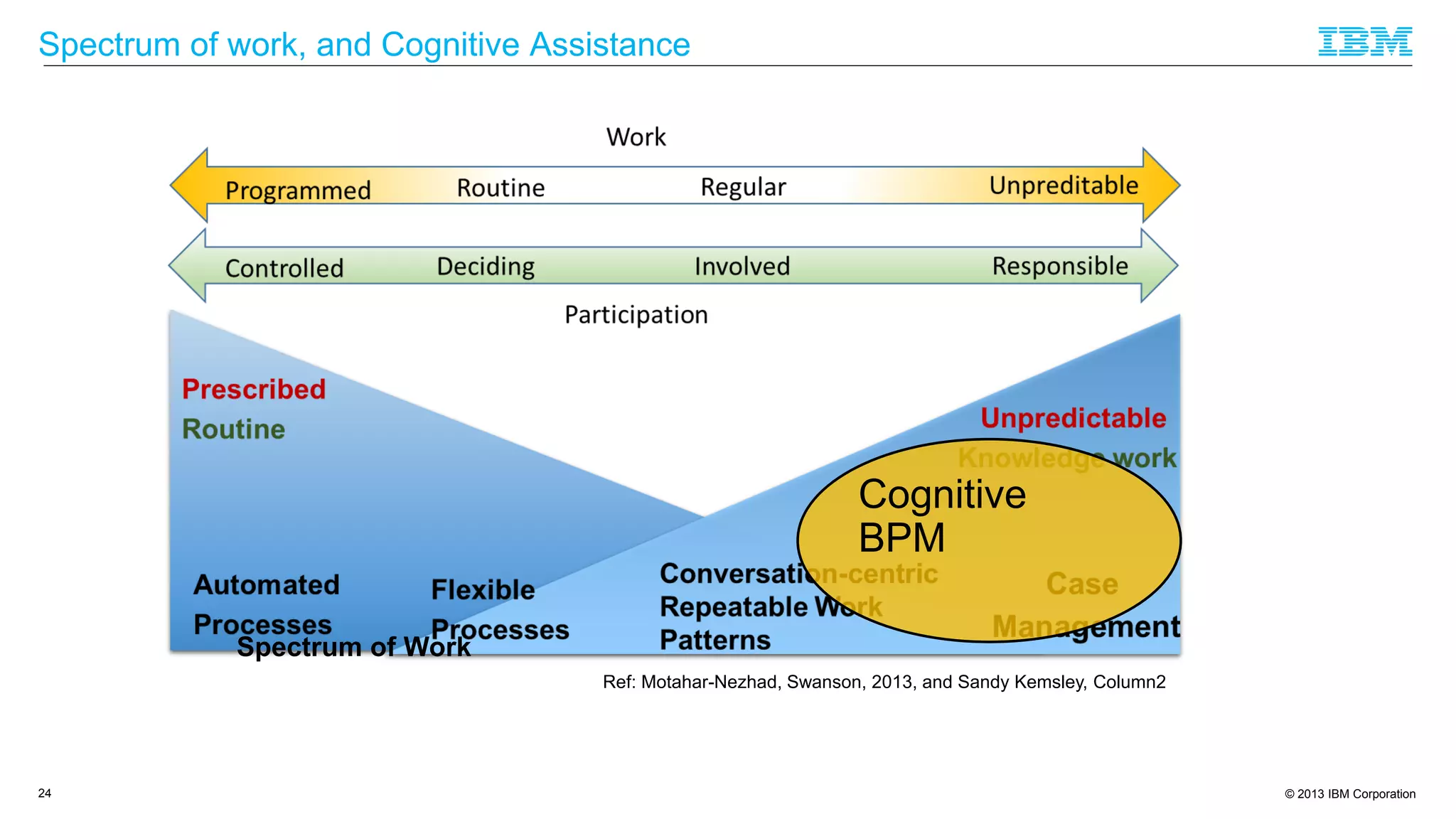
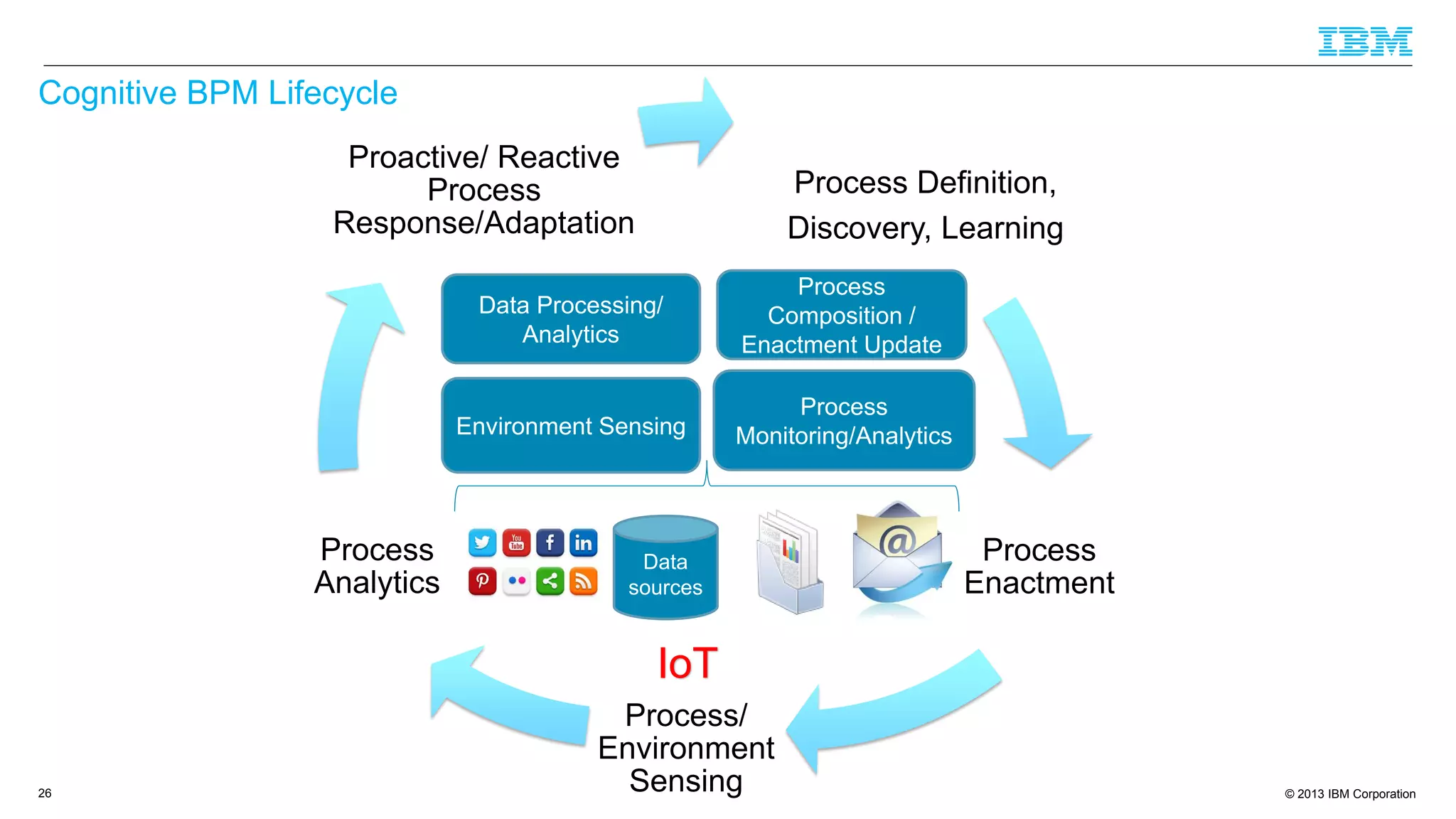
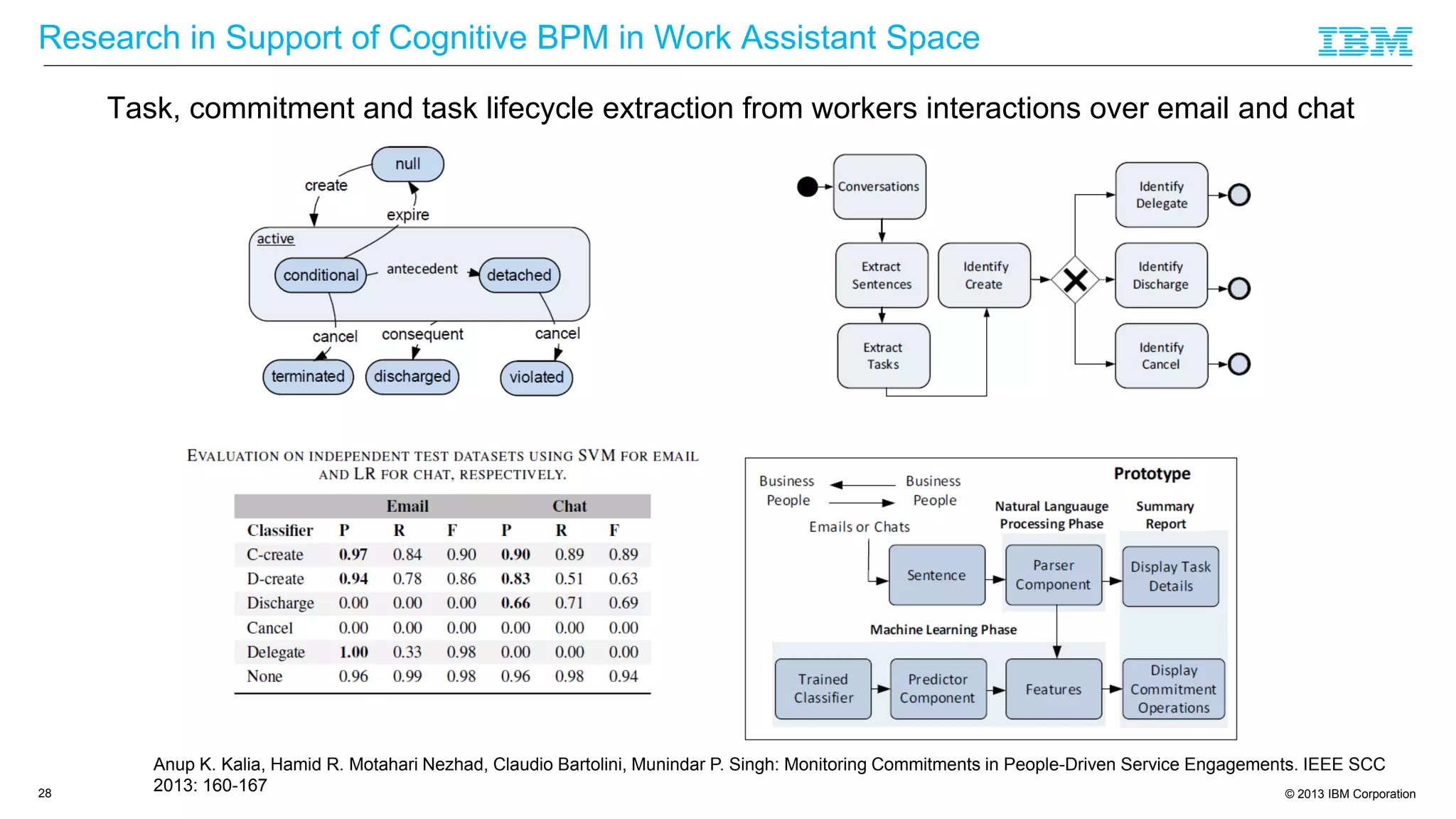
The document discusses cognitive assistance at work, focusing on the role of software agents that augment human intelligence in various administrative tasks such as scheduling, task management, and communication. It highlights the evolution of cognitive assistants from historical AI milestones to modern applications like IBM Watson and personal assistants like Siri and Google Assistant, emphasizing the need for robust knowledge models for effective performance. It outlines the future potential of cognitive assistants to enhance productivity in workplace environments through capabilities such as monitoring, processing information, and supporting decision-making.