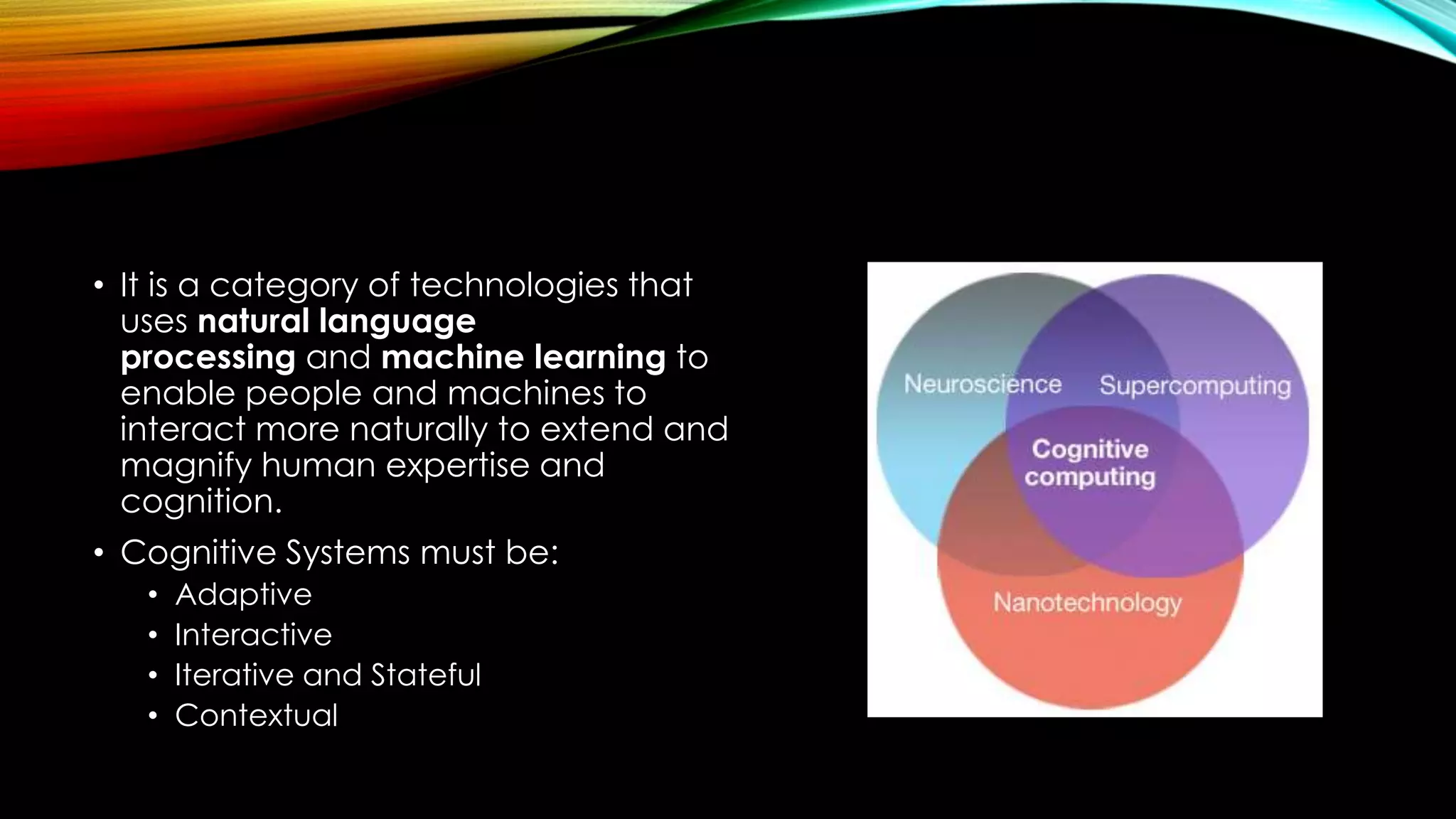
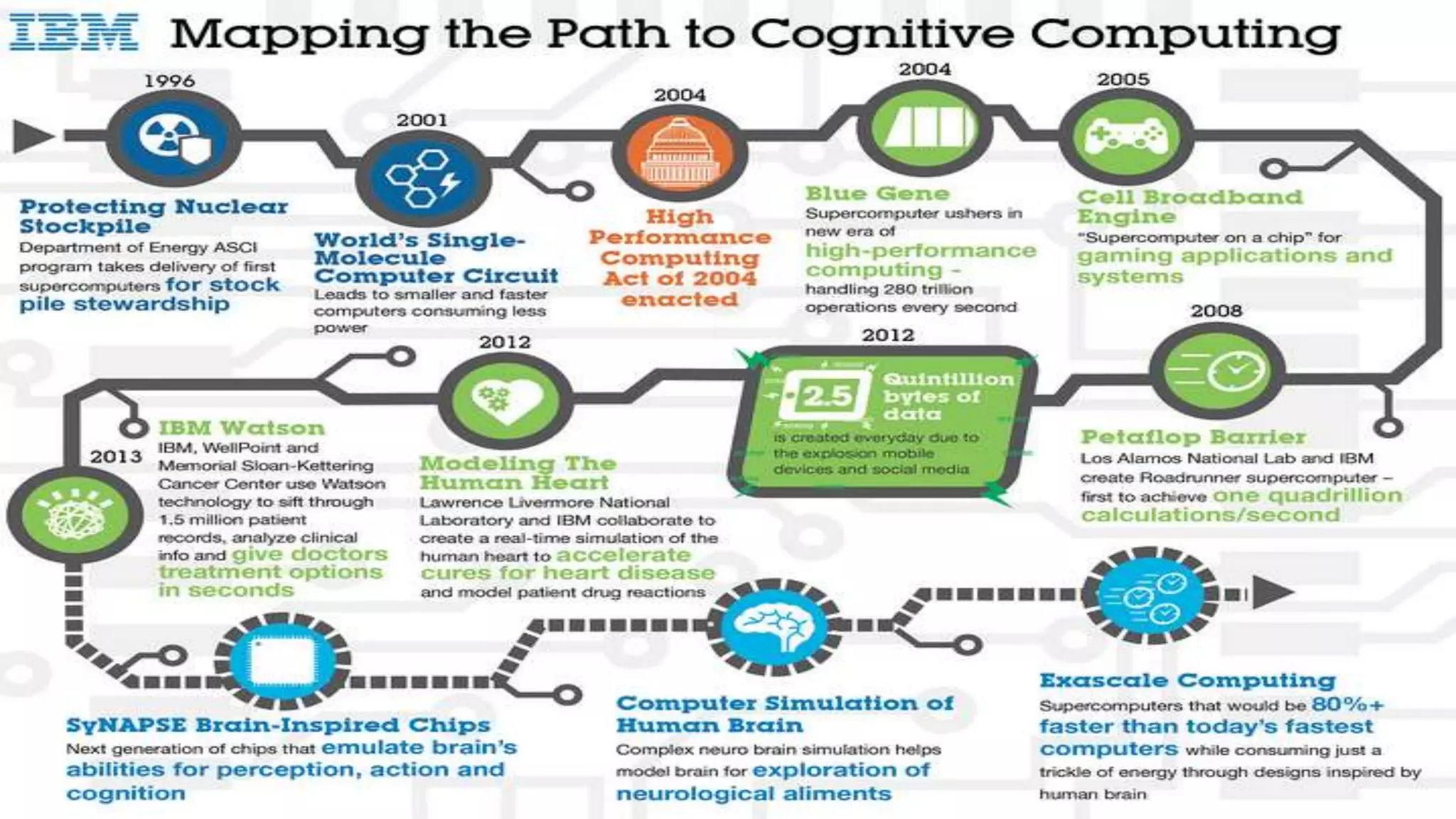
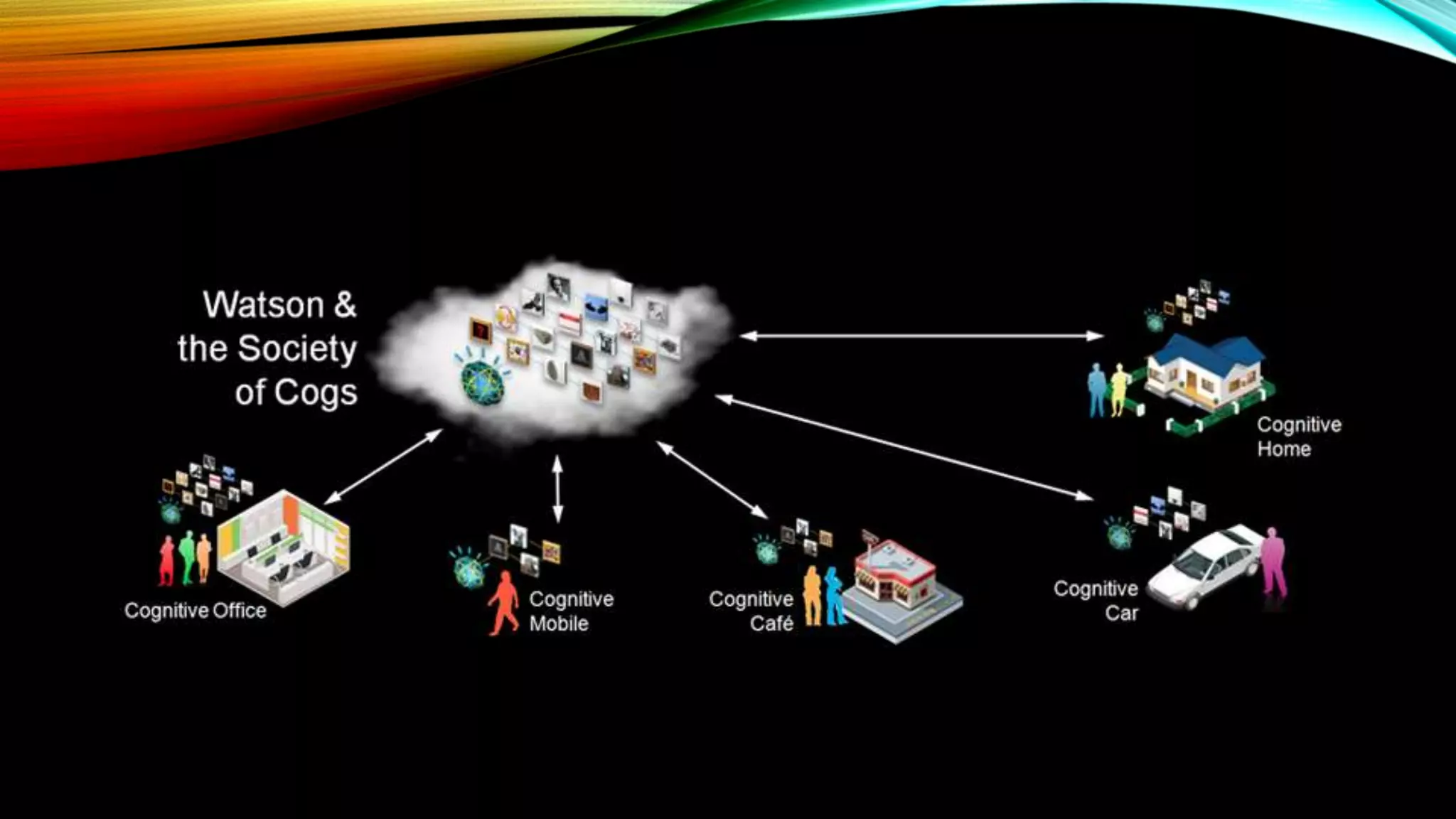
This document discusses cognitive computing and artificial intelligence. It defines cognitive computing as systems that learn from experience and instructions to mimic human cognition by synthesizing information, finding patterns rather than exact answers, and interacting naturally with humans. Specific examples discussed are IBM's Watson, which uses natural language processing and machine learning to answer questions and make complex decisions from vast amounts of data. The document also discusses concerns about the future risks of artificial intelligence, such as superintelligent systems that humans may not be able to control and could ultimately replace humans.