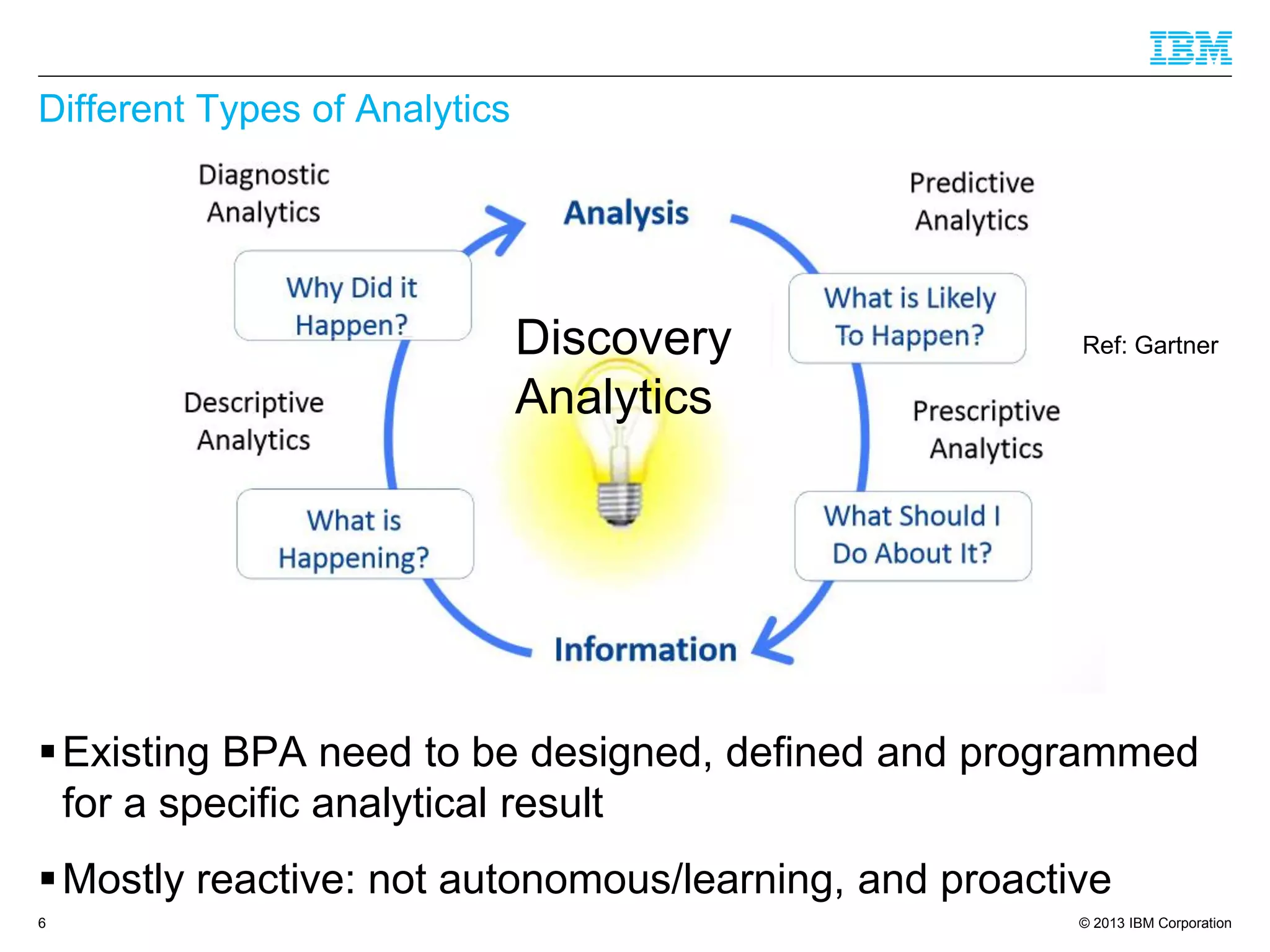
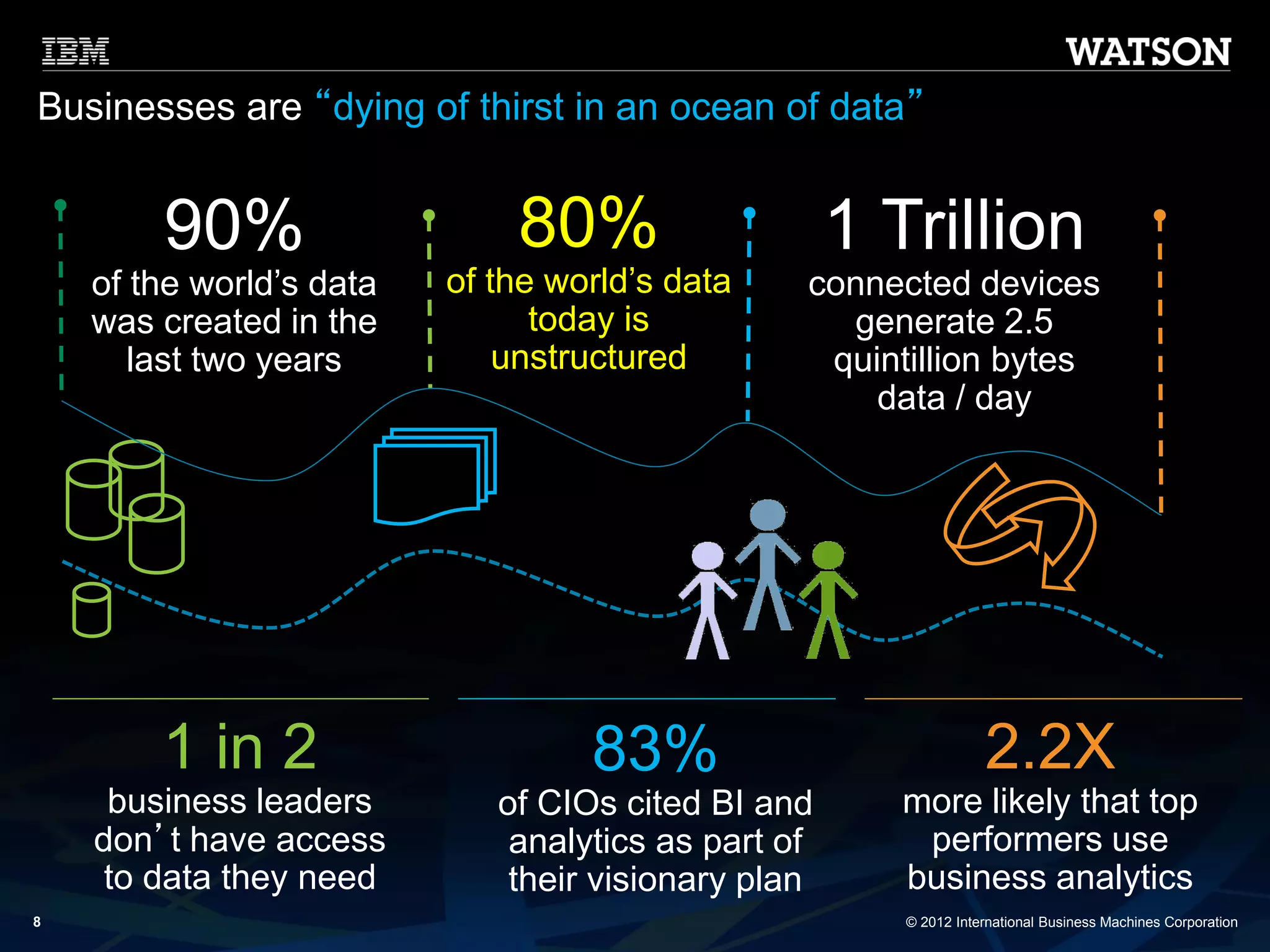
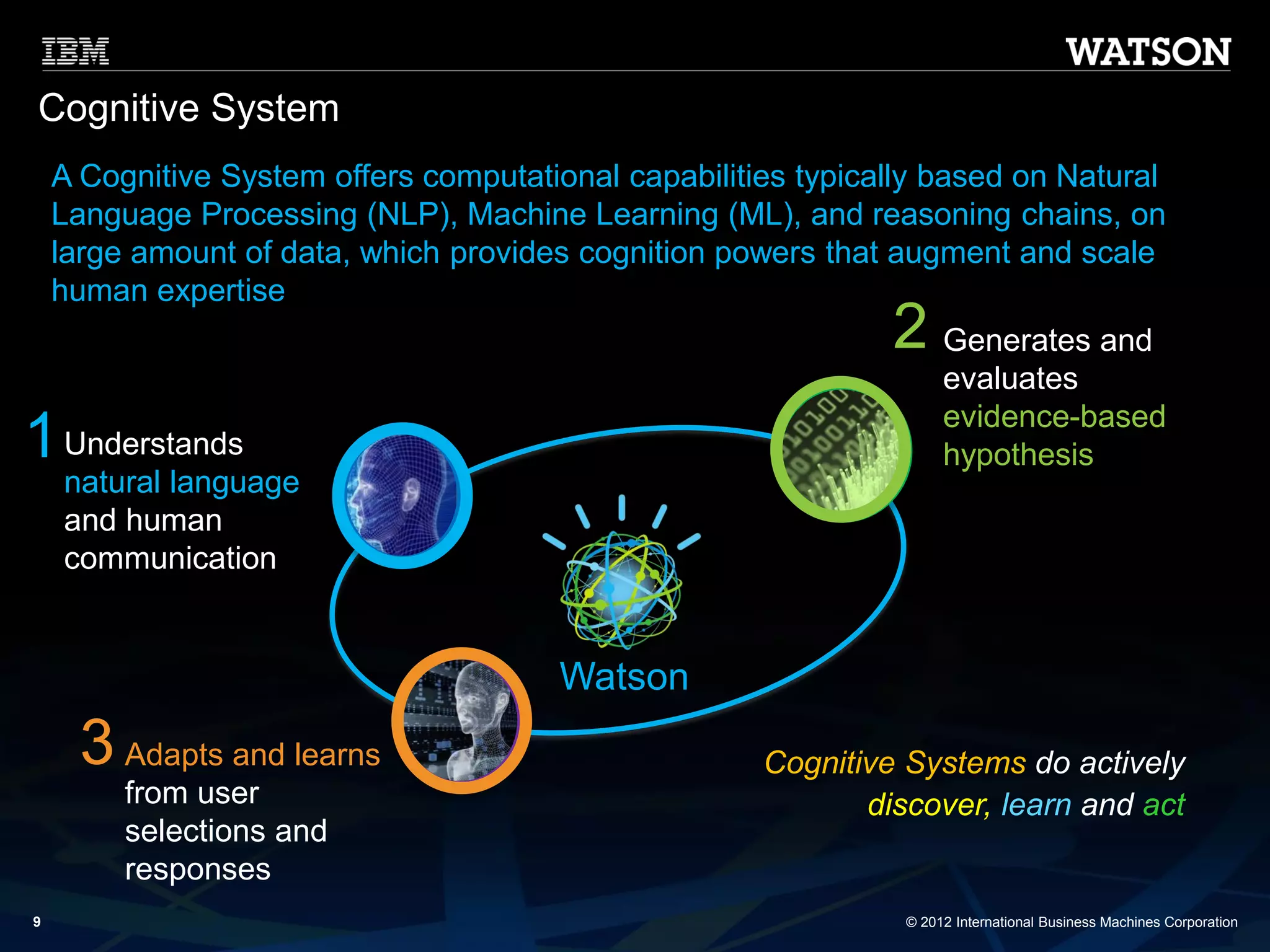
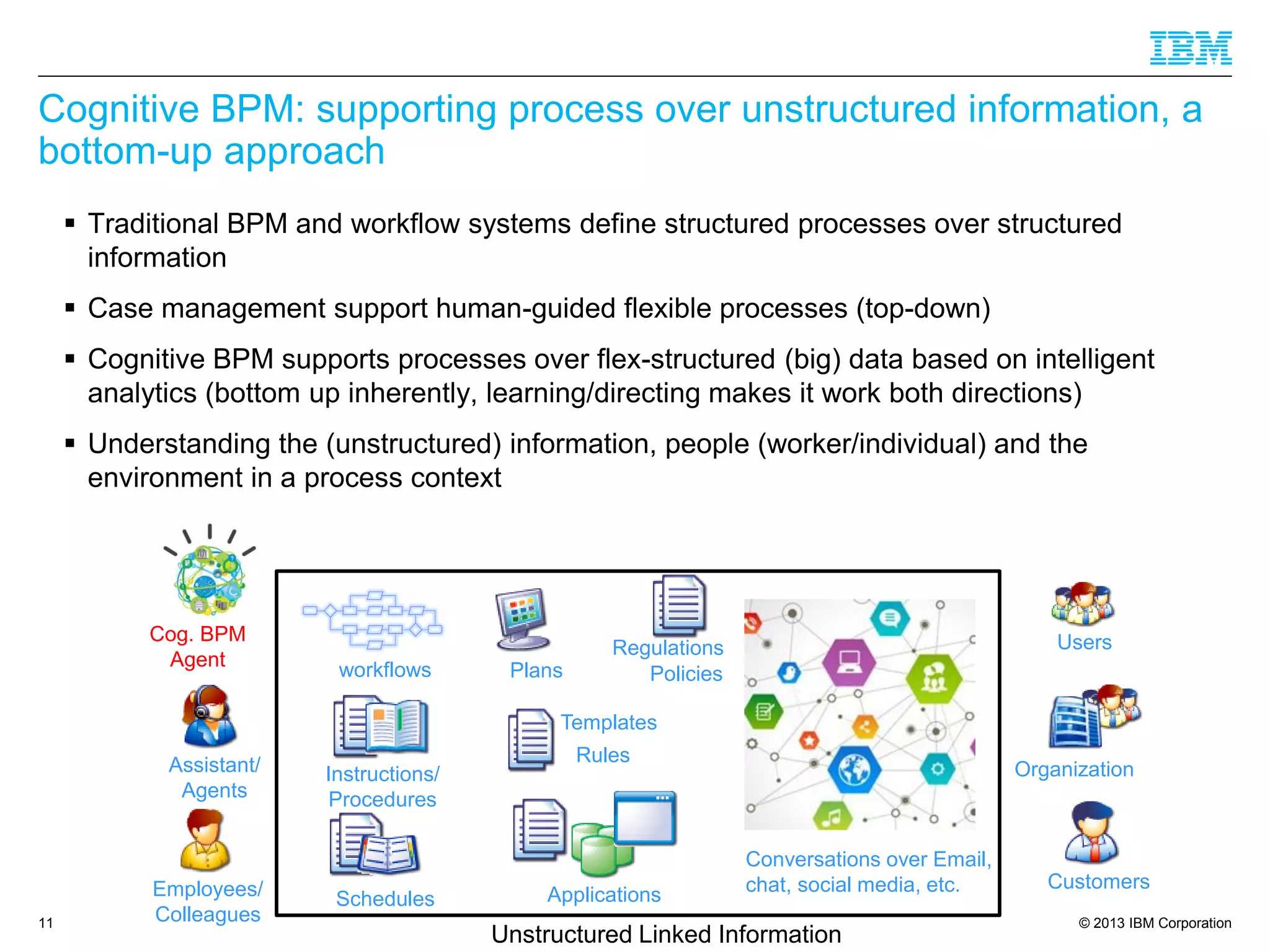
The document discusses the evolution of Business Process Management (BPM) towards Cognitive BPM, emphasizing the integration of analytics and intelligent systems to handle unstructured big data. It outlines how Cognitive BPM can enhance process decisions by leveraging analytics-driven insights, adaptive learning, and proactive responses to emerging data. Furthermore, it presents use cases demonstrating the application of Cognitive BPM in improving efficiency and supporting complex decision-making in various enterprise processes.