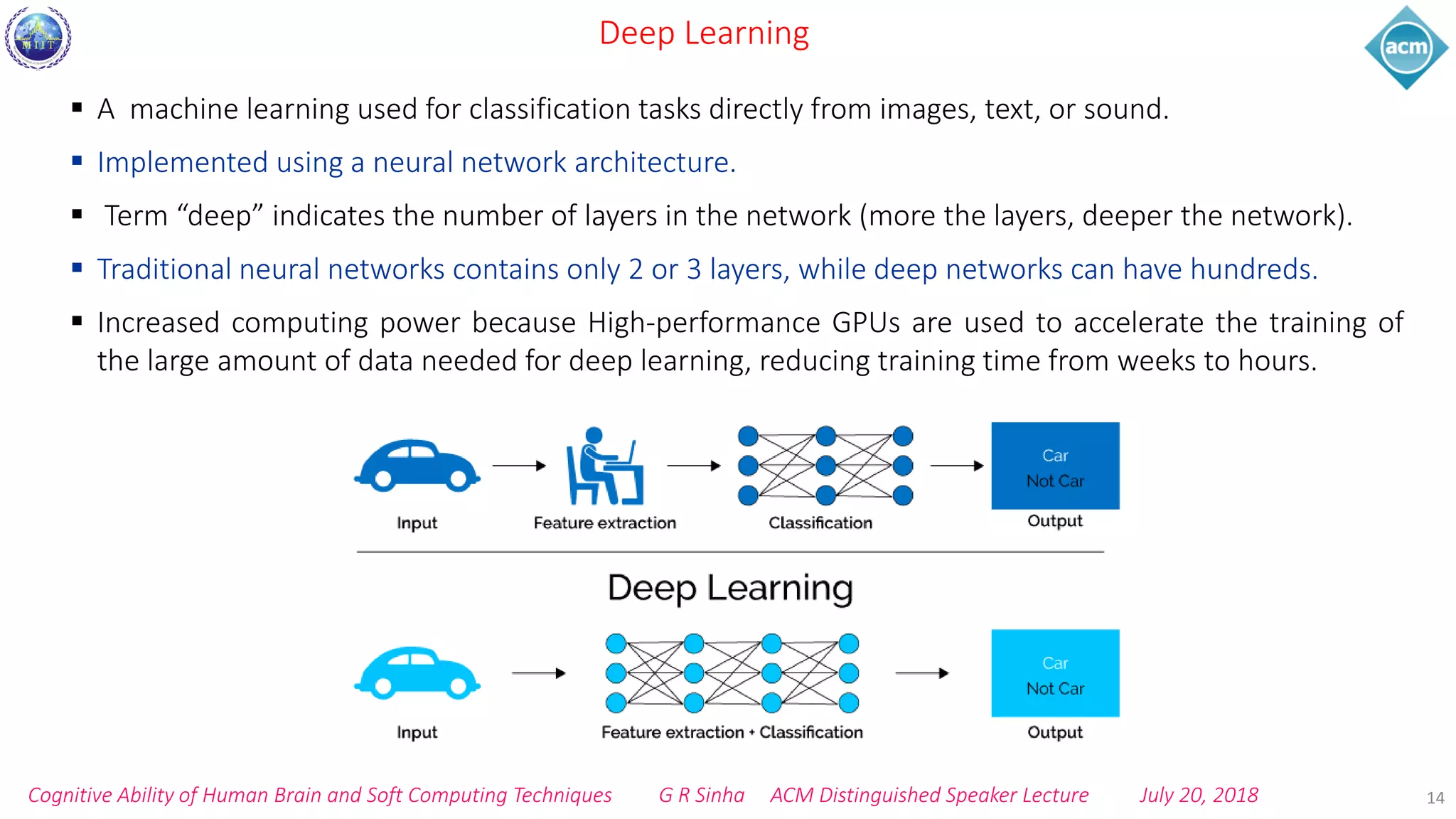
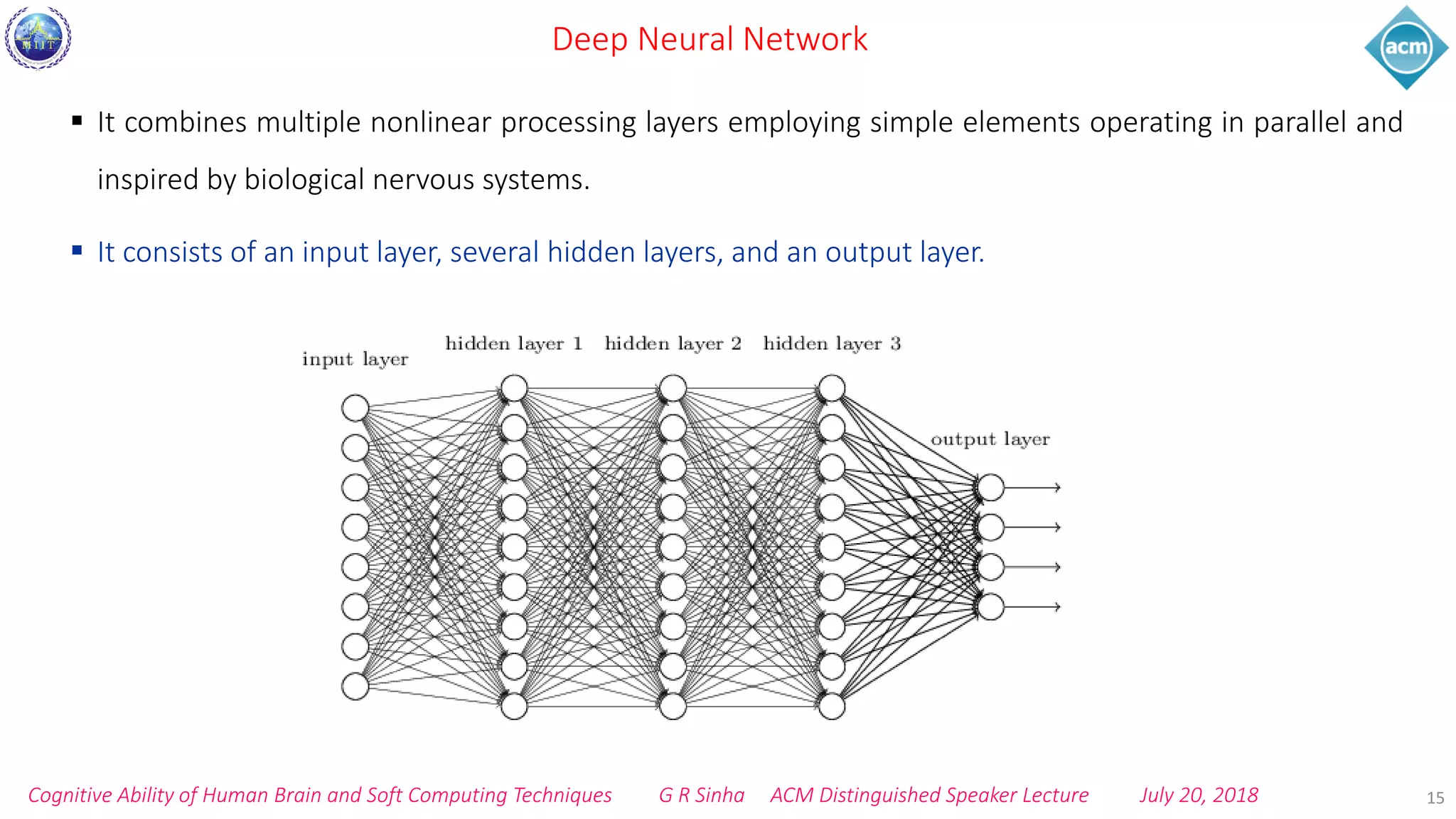
The document discusses cognitive ability of the human brain and soft computing techniques. It begins with providing facts about the brain like the number of neurons and growth rate of neurons. It then discusses cognitive ability development through activities, memory, and experience. Soft computing techniques like neural networks, fuzzy logic, and genetic algorithms are presented as ways to understand cognition through applied neuroscience. Deep learning and convolutional neural networks are specifically highlighted as machine learning approaches for pattern recognition and classification.