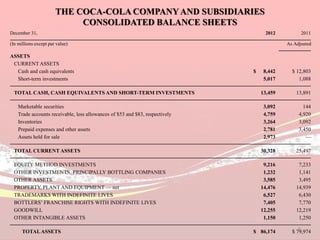
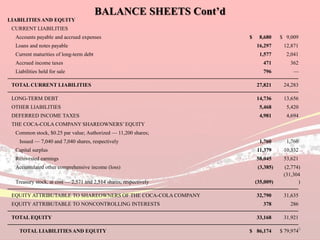
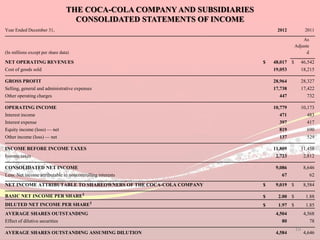
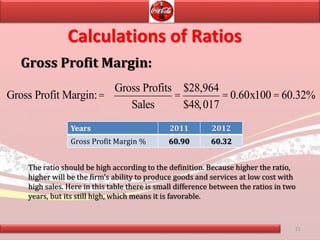
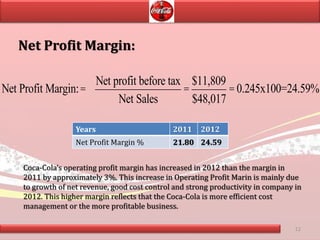
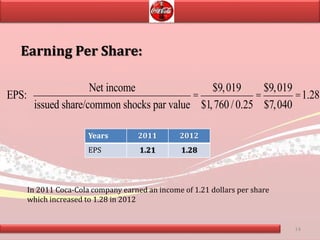
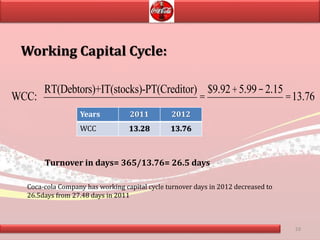
Coca-Cola's financial ratios were analyzed for 2011-2012. The gross profit margin was around 60% both years, indicating efficient cost management. The net profit margin increased from 21.8% to 24.59%, showing greater profitability. Return on capital employed declined slightly from 35.9% to 35.6%. Liquidity ratios like current and quick ratios improved, demonstrating better ability to pay short-term debts. Overall, the analysis found that Coca-Cola remained a profitable company over the two years.