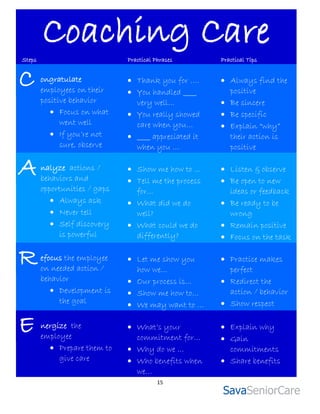
The document discusses coaching as a leadership tool to enhance employee performance. It defines coaching as an informal process of providing guidance, feedback, and encouragement through one-on-one interactions. Coaching benefits include improved performance, goal achievement, and accountability. Effective coaching involves setting expectations, monitoring performance, supporting employees, and recognizing good performance. Leaders should use an authoritative rather than authoritarian style, ask questions instead of telling, and maintain a compassionate and motivational approach.