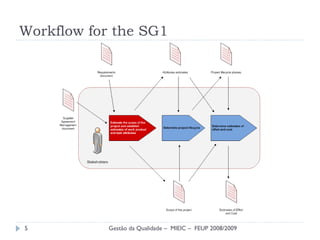
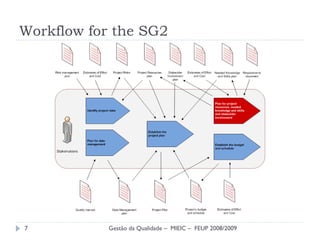
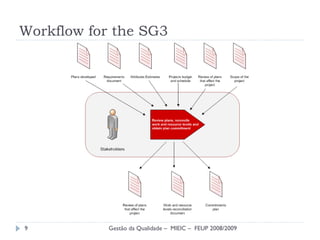
The document presents a final presentation on CMMI Maturity Level 2 Project Planning focused on defining project activities and establishing plans for effective project management. It discusses the development of an ERP software system, detailing specific goals, practices, and risks associated with the project, as well as the importance of stakeholder involvement and skilled staffing. Conclusions emphasize the necessity of a structured approach to project planning to ensure quality, commitment, and effective risk management.