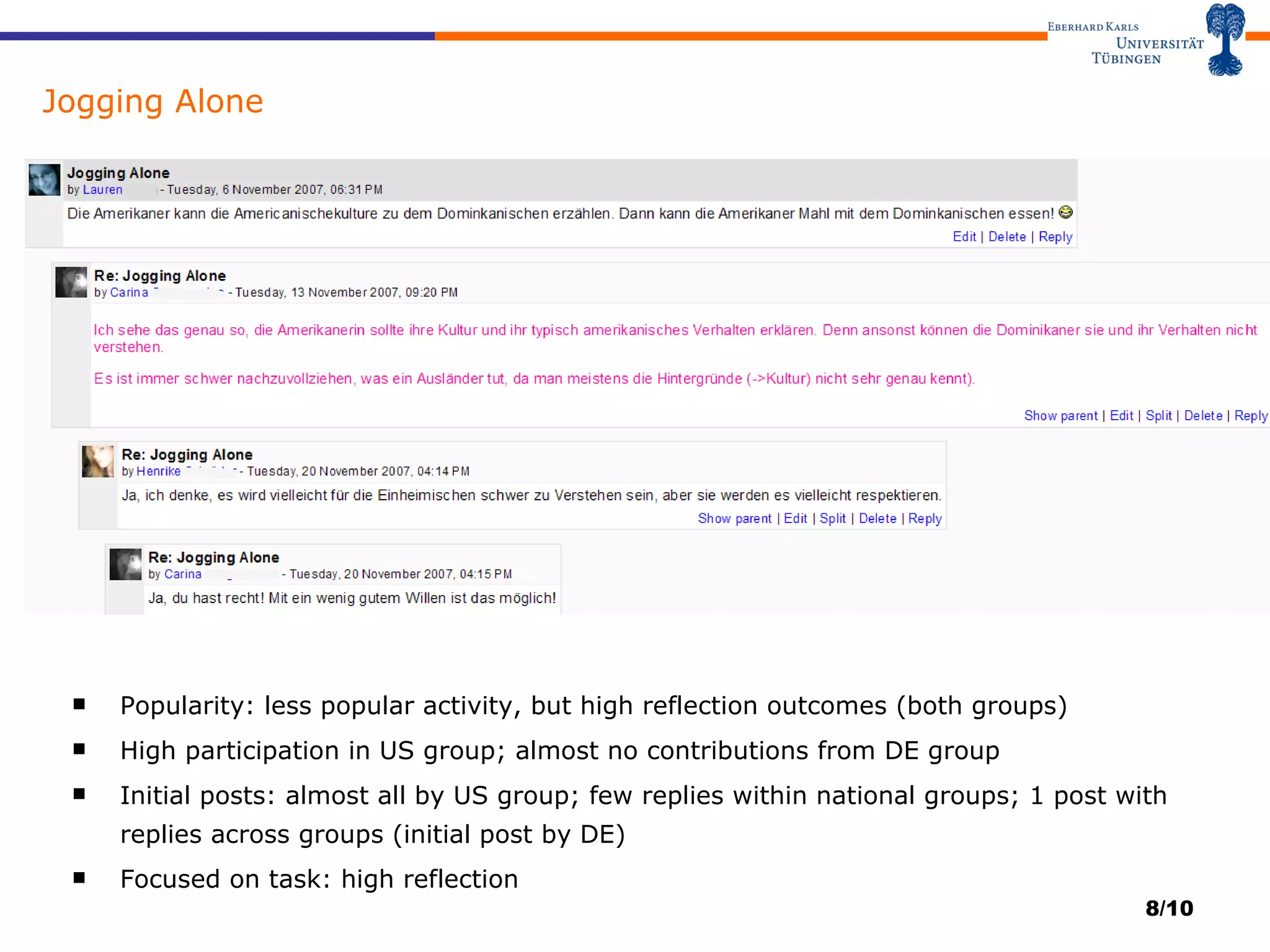
The document discusses using eLearning to improve foreign language skills for intercultural communication. It describes an online exchange program between German and American students taking language classes. The program used a Moodle course platform with various collaborative activities designed to increase intercultural awareness and language skills. An analysis found some tasks appealed more to one group than the other. Factors like class selectivity, novelty, time commitment, and teacher guidance impacted participation and collaboration across groups. The author proposes research questions on how to better design collaborative activities and support web-based intercultural language learning.
![eLearning Scenarios for Language and Culture Integrated Learning Claudia Warth [email_address] University of Tübingen English Department Applied English Linguistics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmcsigclaudiawarthelearningscenarios4-090519115712-phpapp02/75/CMC-SIG-Leon-2009-Claudia-Warth-E-Learning-Scenarios-1-2048.jpg)








![Thank you very much Any questions, input, discussions very welcome! University of Tübingen Applied English Linguistics Claudia Warth Wilhelmstraße 50 D-72074 Tübingen [email_address] http://www.ael.uni-tuebingen.de http://www.spracheundkultur.com/ikkzwei.null /10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmcsigclaudiawarthelearningscenarios4-090519115712-phpapp02/75/CMC-SIG-Leon-2009-Claudia-Warth-E-Learning-Scenarios-11-2048.jpg)
