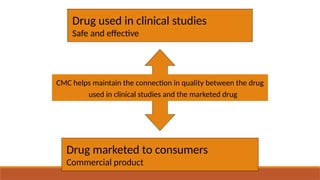
The document presents an overview of Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Control (CMC) and post-approval regulatory affairs, emphasizing their critical roles in ensuring drug quality and safety during development and after approval. It details the essential elements of CMC, including manufacturing processes, quality attributes, and regulatory requirements for compliance. Moreover, it outlines post-approval changes categories, associated reporting requirements, and recommendations for maintaining drug quality post-marketing.