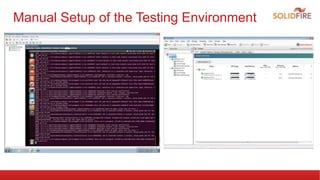
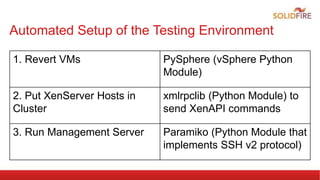
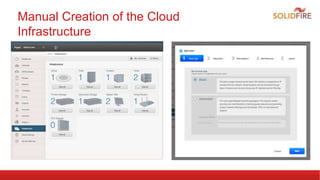
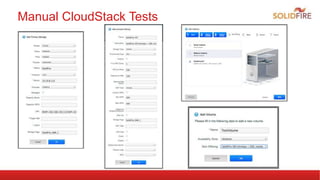
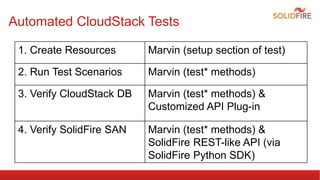
The document discusses automated integration testing for CloudStack using Marvin, a Python testing framework, which simplifies creating custom cloud environments and executing API commands. It details the setup of a testing environment with various virtual machines and outlines both manual and automated procedures for creating cloud infrastructure and running test scenarios. Future enhancements include nightly tests using Jenkins and integration tests for additional virtualization environments.