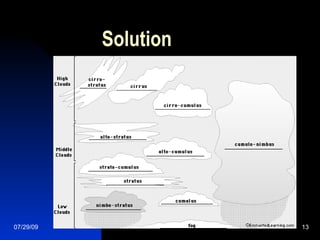
There are three main requirements for cloud formation: moisture, cooling air, and condensation nuclei. Moisture is provided by water vapor in the air. Cooling is needed for the water vapor to condense, which often occurs at high altitudes where the air is cooler. Condensation nuclei like dust and smoke particles provide surfaces for water molecules to gather and condense into water droplets. Clouds are classified by their altitude and appearance, with cirrus being high wispy clouds and cumulus being lower puffy clouds. Cumulonimbus clouds can produce thunderstorms.