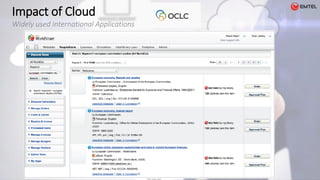
This document summarizes a workshop on cloud computing for librarians. The session aims to provide an introductory overview of cloud computing concepts and benefits through videos, graphics and interactions rather than lengthy presentations. The agenda covers definitions of cloud computing, origins and service/deployment models. Key benefits discussed are reduced costs, flexibility and scalability compared to traditional infrastructure. Major cloud providers mentioned include Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure and Rackspace. The document concludes that cloud computing provides utilities like access to data, hardware and support anywhere and anytime at lower costs, and that librarians should not fear cloud technology due to its widespread adoption and benefits.

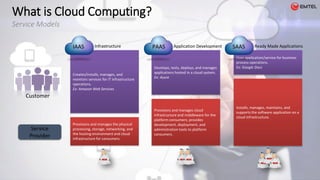
![What is Cloud Computing ?
Definitions
NIST [National Institute of Standards and Technology]:
• Cloud computing is a model
• for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access
• to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers,
storage, applications, and services)
• that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or
service provider interaction.
1. On-demand self-service
2. Broad network access
3. Resource pooling
4. Rapid elasticity
5. Measured service
• This cloud model is based on
• 3 Service Models [IaaS | Paas | SaaS]
• 4 Deployment Models [Public | Private | Hybrid | Community]
Cloud
Computing
Cloud
Abstraction
“System’s Approach”
Processing of Information
Computing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputingv3mar2016-160407185158/85/Cloud-computing-v3-mar-2016-4-320.jpg)

![What is Cloud Computing?
Deployment Models
Network Applications
Infrastructure
Community Cloud: Used for a single
organization; can be internally or
externally hosted
Hybrid Cloud: Composition of two or
more clouds [private, community or
public] that remain unique entities but
are bound together, offering the
benefits of multiple deployment models
Private Cloud: Shared by several
organizations; typically externally hosted
but may be hosted by one of the
organization
Public Cloud: Provisioned for open use
by a particular organization who hosts
the service
A model for enabling
ubiquitous network access
to a shared pool of
configurable computing
resources.
Types of Cloud Deployment Overlap between Models](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputingv3mar2016-160407185158/85/Cloud-computing-v3-mar-2016-7-320.jpg)


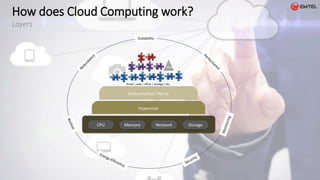


![Who is involved in Cloud Computing?
International Service Providers
Amazon Web Services [AWS]:
• Diverse customer base
• Broadest range of use cases, including enterprise and
mission-critical applications.
• >10 times more cloud IaaS compute capacity in use than
the aggregate total of the other 14 providers in this
Magic Quadrant.
MicroSoft Azure:
• Leverages on
• Microsoft's brand,
• Existing customer relationships,
• History of running global-class consumer Internet properties,
• Deep investments in engineering,
• Aggressive roadmap
• To rapidly to attain the status of strategic cloud IaaS
provider
RackSpace:
• Rackspace offers
• Multitenant OpenStack-based public cloud
• 3 flavors of hosted private cloud](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputingv3mar2016-160407185158/85/Cloud-computing-v3-mar-2016-19-320.jpg)



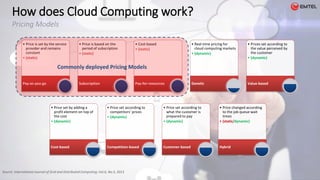
![• Data Accessibility
• Anywhere
• Anyhow
• Anytime
• Costs
• License [Google Docs @ $ 0 v/s MS Office $ 200]
• Unlimited Hardware
• No Hassle
• Support & Maintenance
• Future Proof
Impact of Cloud
Personal & Existing Librarian Area](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputingv3mar2016-160407185158/85/Cloud-computing-v3-mar-2016-24-320.jpg)