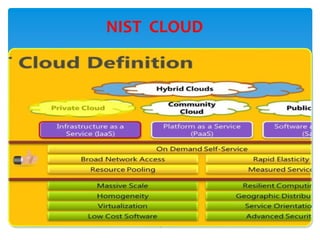
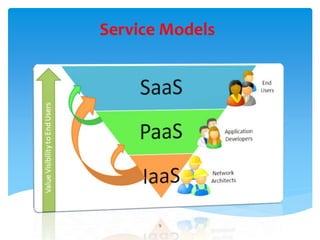
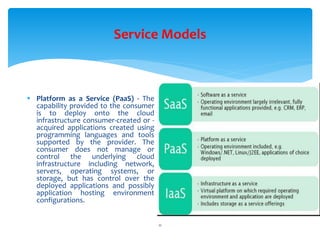
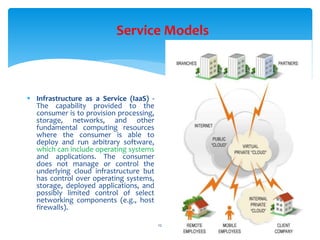
Cloud computing is defined as the on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources, allowing users to rent applications and infrastructure over the internet. It features five essential characteristics, including self-service, broad access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service, as well as three service models: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. The document also briefly introduces i-softinc as a notable mobile application development company in the USA.