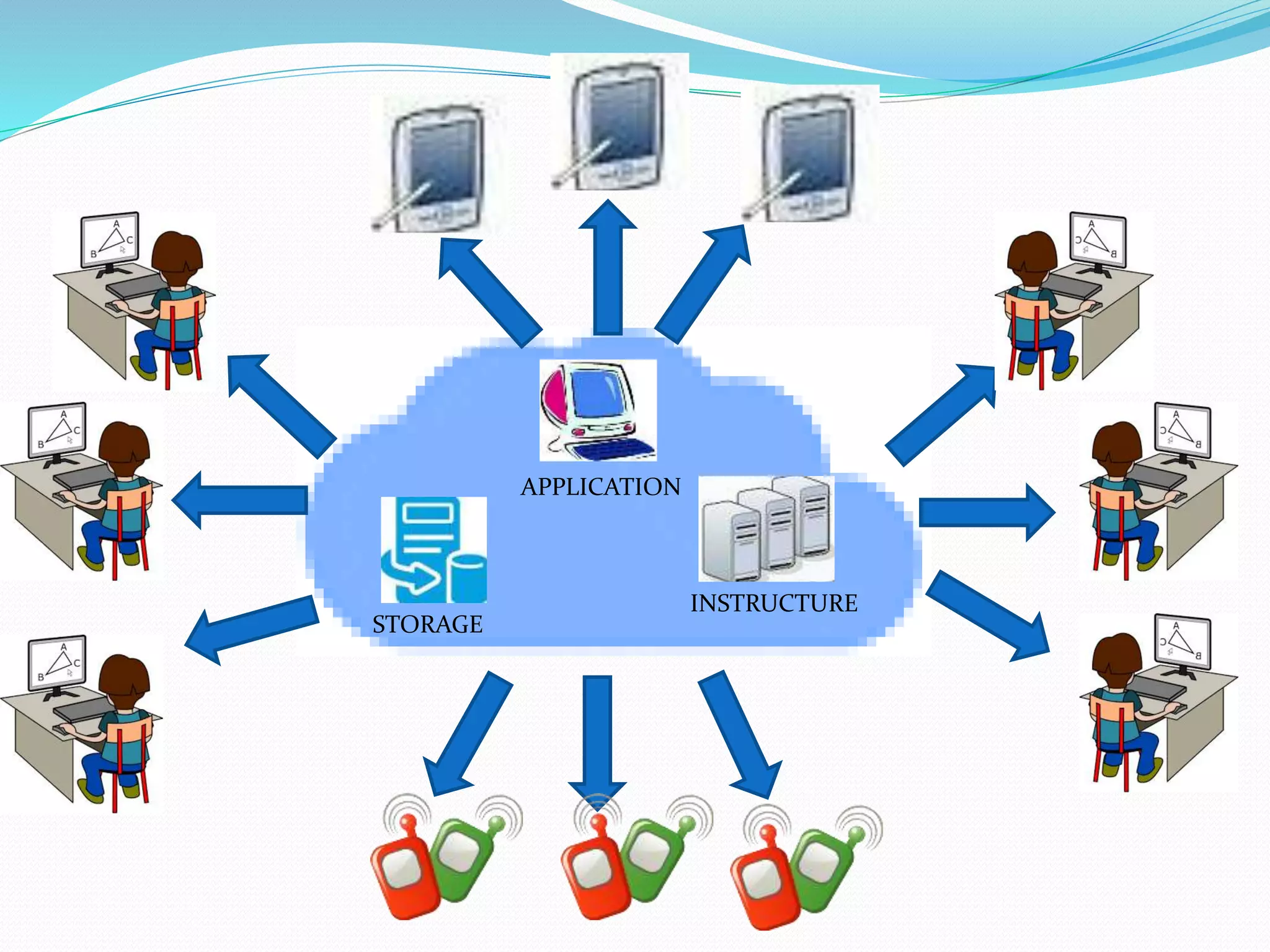
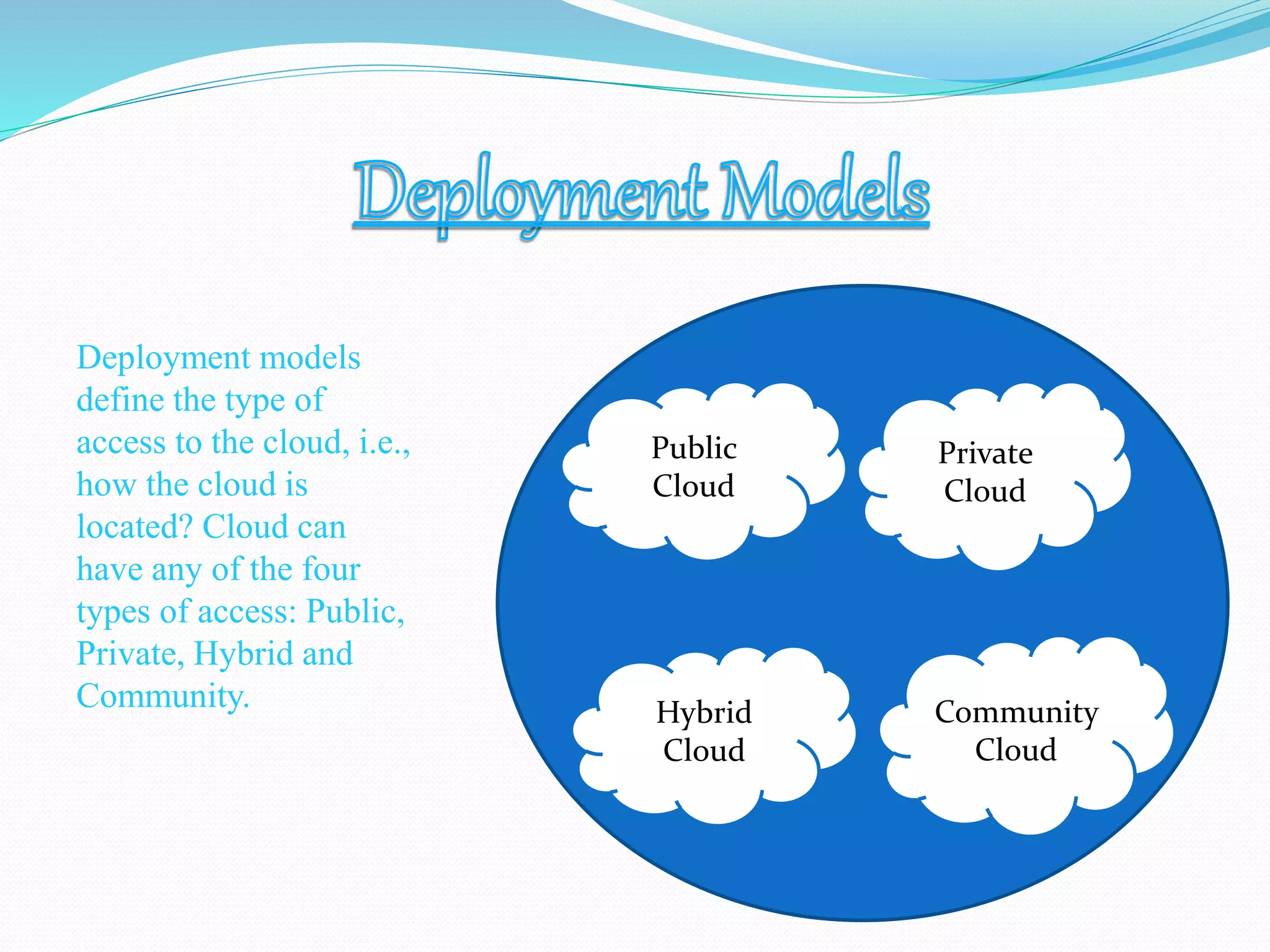
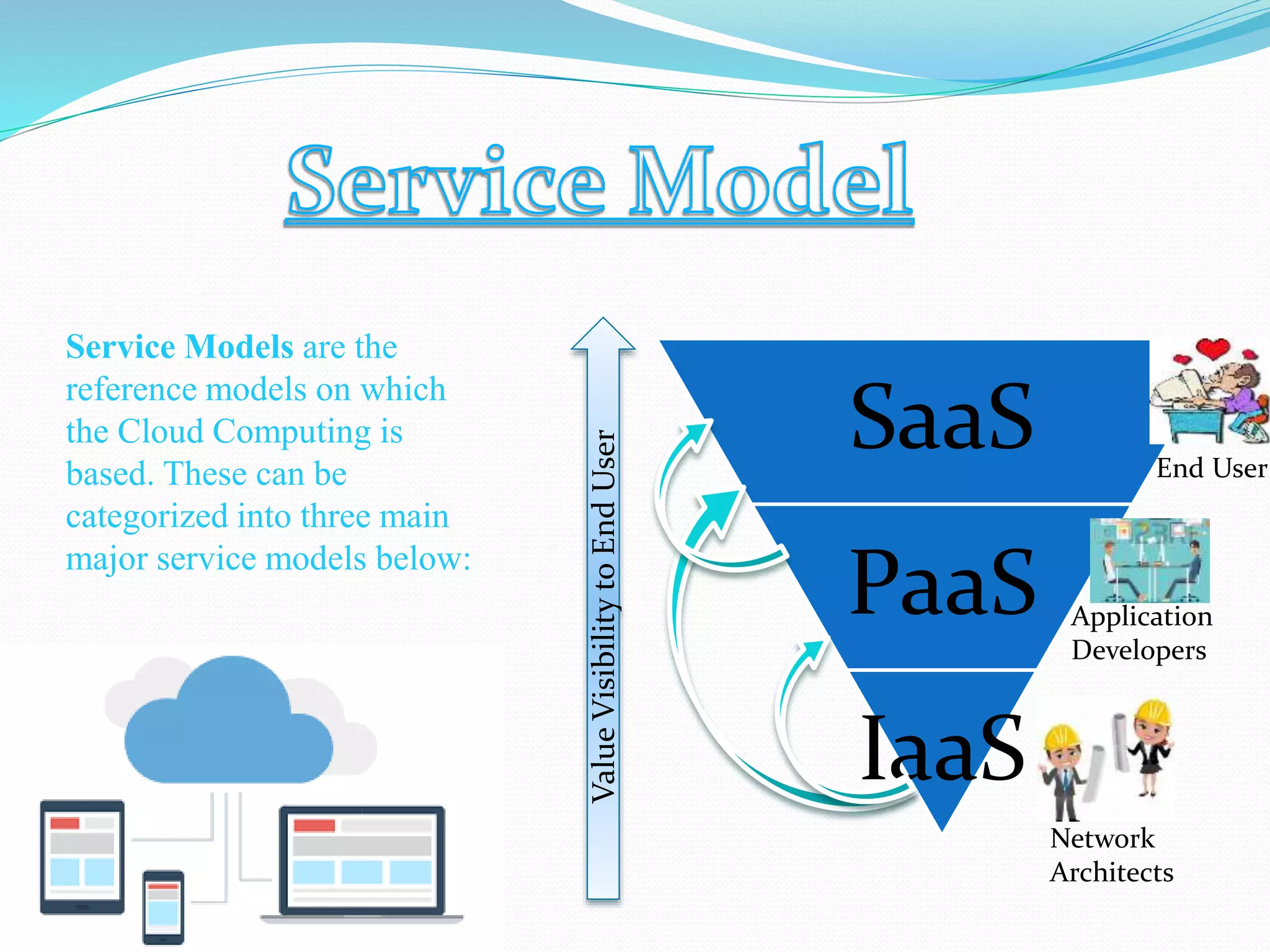
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, defining it as accessing and manipulating applications and data through the internet. It explains cloud deployment models (public, private, hybrid, and community) and service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) that manage access and resources, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of using cloud services. Understanding these concepts helps users choose the right solutions based on their needs for security, scalability, and flexibility.