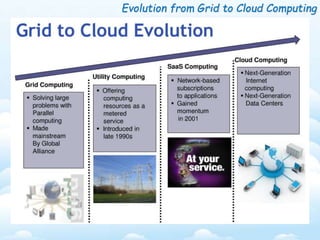
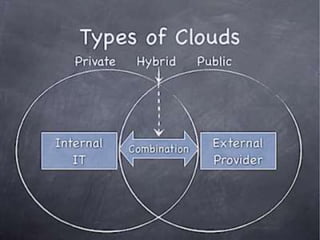
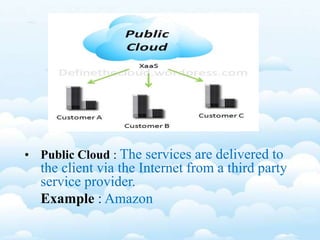
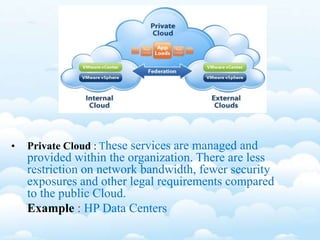
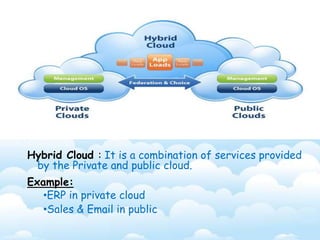
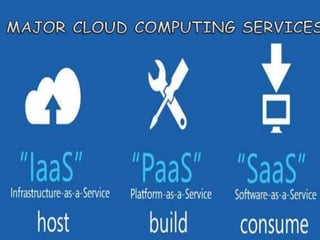
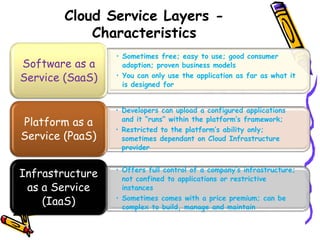
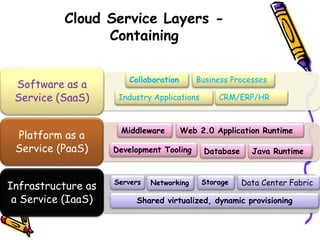
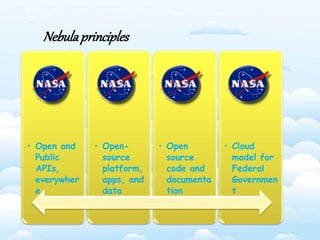
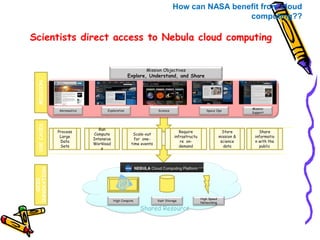
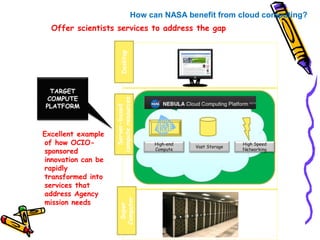
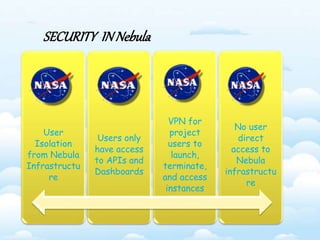
The document outlines the fundamental concepts and benefits of cloud computing, detailing its history, types (public, private, hybrid), and service layers (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS). It emphasizes the significance of cloud computing for organizations like NASA, highlighting how it can enhance their computational capabilities and data management. The text also discusses various applications and future potential within educational contexts.