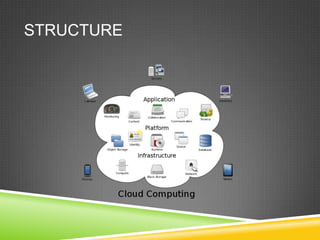
This document provides an introduction to cloud computing and examples of cloud services. It defines cloud computing as the delivery of computing resources as a service over the internet. It discusses public, private and community cloud models. It then gives examples of cloud services for data storage (Amazon S3), computing (Amazon EC2), productivity (Google Docs), finance (Mint), libraries (Consuls), databases (EbscoHost), and administration (Banner). The assignment is to create a Google Docs account and share a document.