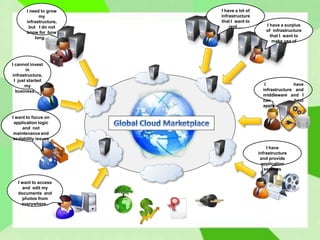
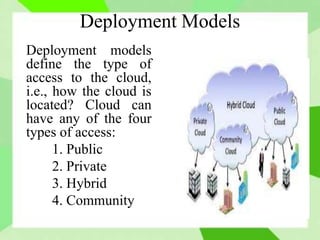
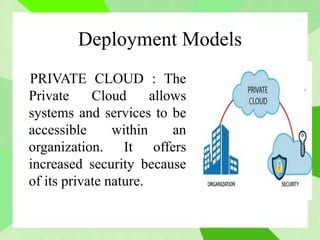
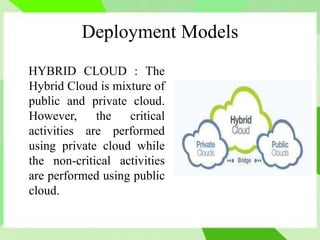
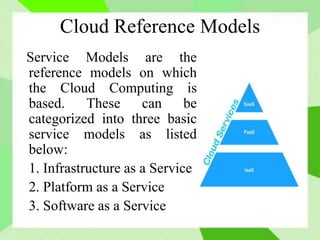
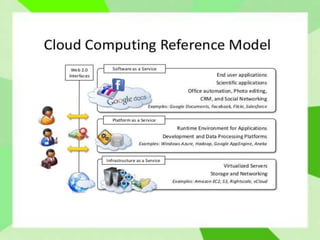
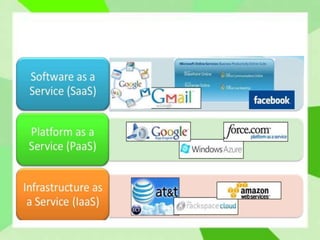
Cloud computing allows users to access computing resources like storage and infrastructure over the internet from anywhere. It provides on-demand access to virtual hardware, platforms, and applications without users having to manage the underlying infrastructure. The main models of cloud computing are deployment models (public, private, hybrid, community clouds) and service models (Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, Software as a Service). Cloud computing offers advantages like flexible scaling, lower costs, and simplified application development, but also poses challenges around security, performance, and reliability.