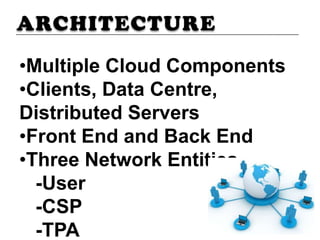
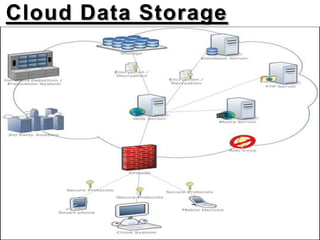
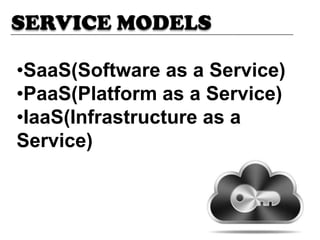
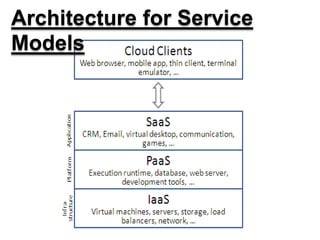
This document discusses security threats and countermeasures related to cloud computing. It begins with an introduction to cloud computing, describing its key characteristics and benefits. It then outlines several common cloud computing deployment and service models. The document identifies several security threats to cloud computing such as insecure APIs, data leakage, and network sniffing. It proposes remedies for each threat, including strong authentication, encryption, and access control. Finally, it concludes that while cloud computing provides many benefits, it is vulnerable to security risks that can be lessened through security measures.