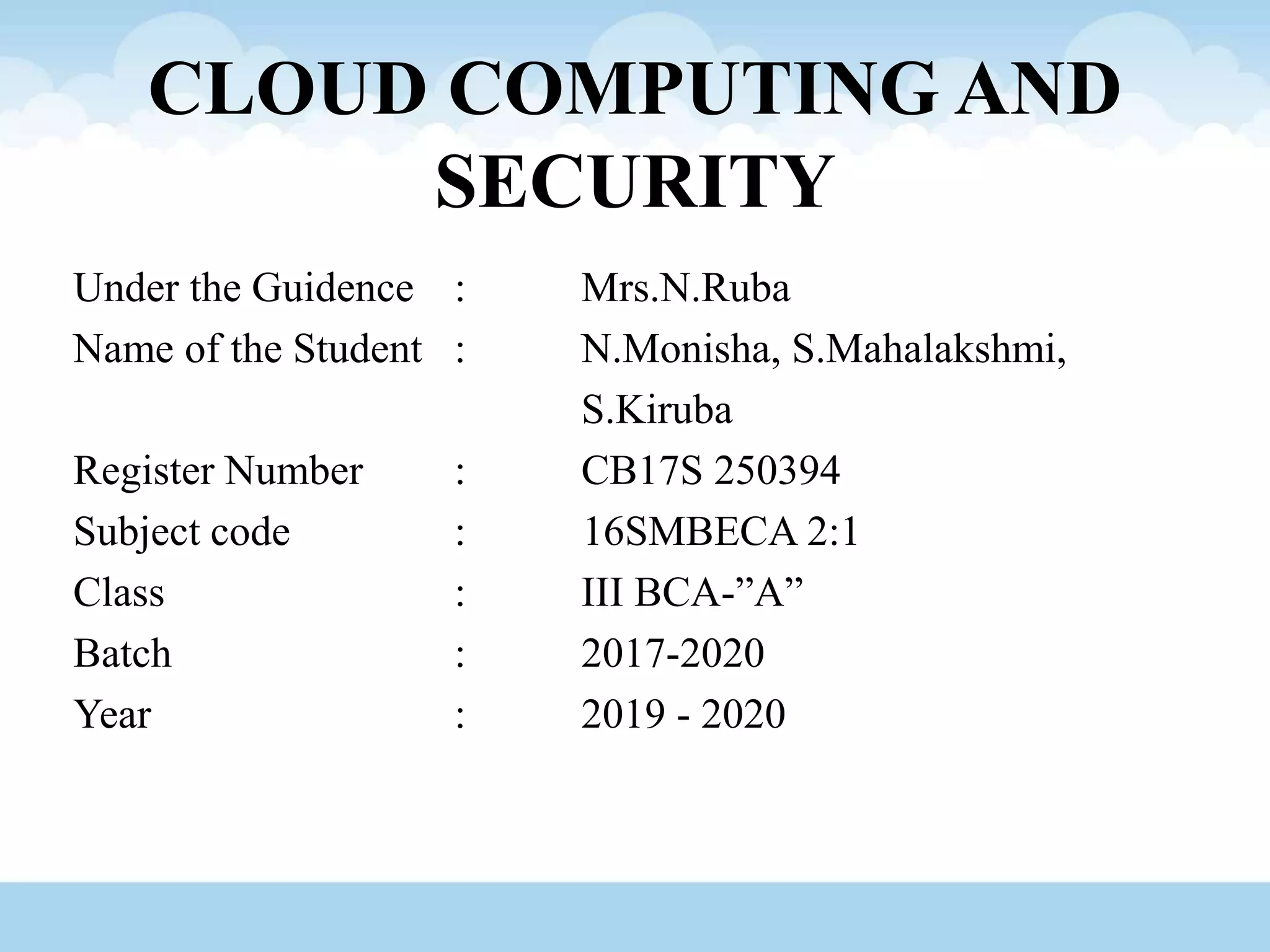
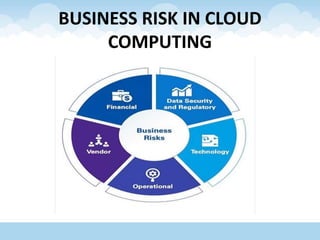
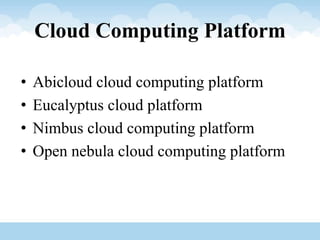
The document discusses various aspects of cloud computing and security, covering risks, security advantages and disadvantages, and data management strategies. It emphasizes the significance of data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, alongside outlining tools and technologies like Hadoop and VMware. The text also explores the evolution of content level security and the importance of disaster recovery plans in cloud environments.