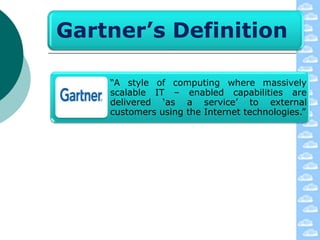
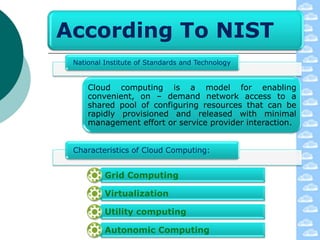
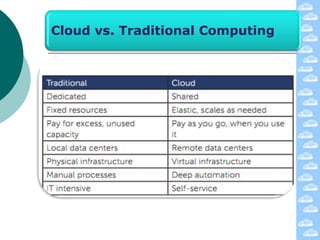
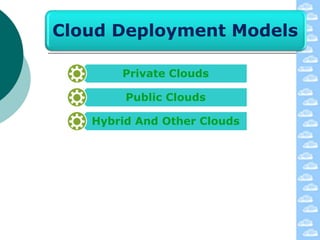
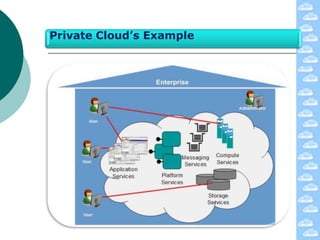
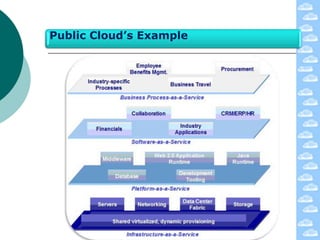
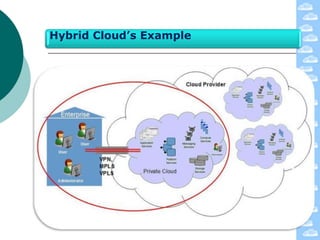
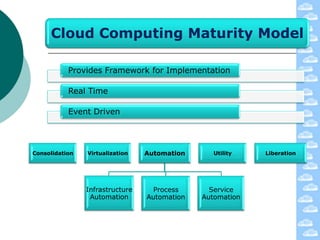
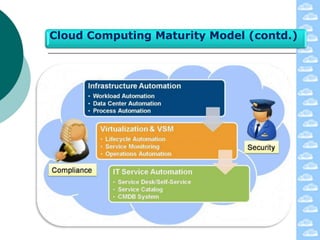
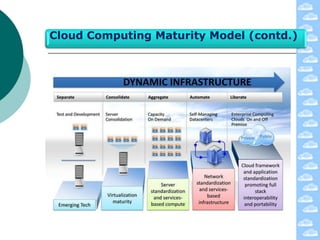
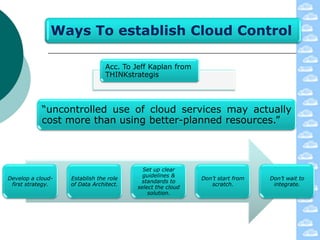
The document discusses cloud computing and its deployment models. It defines cloud computing according to NIST and Gartner and explains its characteristics including grid computing, virtualization, utility computing, and autonomic computing. It describes private, public, and hybrid cloud deployment models and provides examples. The document also discusses establishing cloud control through developing strategies and standards. It outlines reasons to consider and avoid adopting cloud computing.