The document presents an internship report on the development of a Clothes Store Management System aimed at automating existing manual processes to enhance efficiency, reliability, and user experience. The system is equipped with various modules for managing inventory, payments, and product details, and is designed to minimize data entry errors and improve access to information. It also includes a Software Requirements Specification (SRS) to guide the development and ensure the final product meets user expectations.











![16 | P a g e
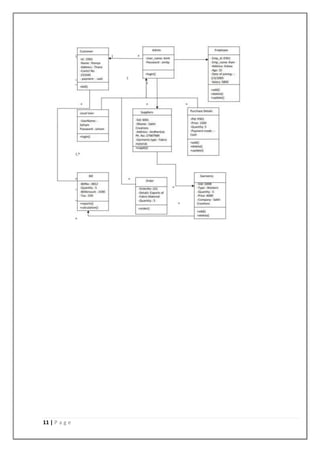
Source code
#include<fstream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
class dress{
private:
char filename[20]; protected:
char dressname[60];
char dressid[10]; float
price;
void get();
};
void dress::get()
{
cout<<"n ENTER DRESS NAME : ";
cin>>dressname;
cout<<"n ENTER DRESS ID NO : ";
cin>>dressid;
cout<<"n ENTER DRESS PRICE : ";
cin>>price;
strcpy(filename,dressid);
strcat(filename,".txt");
ofstream x(filename);
x<<"nnDRESS NAME :"<<dressname;
x<<"nnDRESS ID :"<<dressid;
x<<"nnPRICE :"<<price;
x.close();
}
class male:protected dress
{
public:
male();
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clothesstoremanagementsystemprojectreport-240809082420-eb54ae23/85/Clothes-store-management-system-project-report-pdf-16-320.jpg)



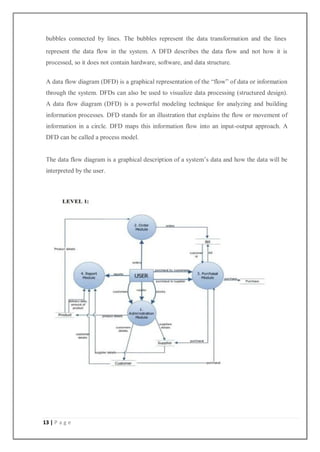
![20 | P a g e
getch();
}
if(m==2)
{
ifstream m("FEMALE.txt");
while(m)
{
m.get(ch);
cout<<ch;
}
getch();
}
if(m==3)
{
ifstream m("CHILD.txt");
while(m)
{
m.get(ch);
cout<<ch;
}
getch();
}
if(m==4)
{
char id[10],filename[20];
cout<<"input id for search:";
cin>>id;
strcpy(filename,id);
strcat(filename,".txt");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clothesstoremanagementsystemprojectreport-240809082420-eb54ae23/85/Clothes-store-management-system-project-report-pdf-20-320.jpg)
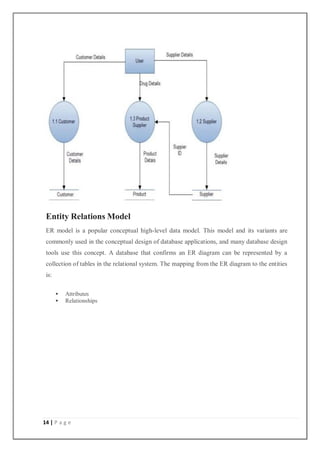
![21 | P a g e
ifstream m(filename);
while(m)
{
m.get(ch);
cout<<ch;
}
getch();
}
if(m==5)
break;
}
}
class cut{
public:
cut();
};
cut::cut()
{ char id[20],filename[20];
cout<<"nnEnter the id to delete : ";
cin>>id;
strcpy(filename,id);
strcat(filename,".txt"); fstream
x(filename,ios::out);
x<<"INFORMATION IS UNAVALABLE";
x.close();
}
int main()
{
int i;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clothesstoremanagementsystemprojectreport-240809082420-eb54ae23/85/Clothes-store-management-system-project-report-pdf-21-320.jpg)