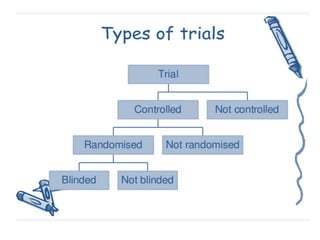
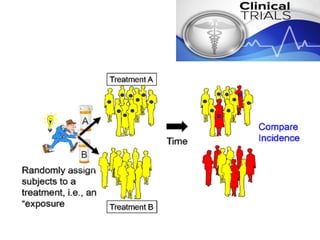
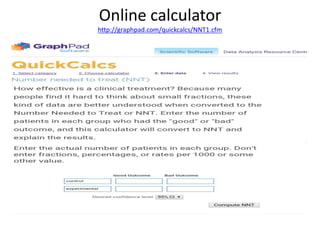
This document discusses random allocation and concealment in medical trials. It defines the Number Needed to Treat (NNT) as the number of patients who need to be treated to prevent one bad outcome. The NNT is calculated from the Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR) as the inverse of the ARR. An example calculation is provided. Benefits of the NNT are that it provides a more clinically useful measure than other statistics like relative risk. The Number Needed to Harm (NNH) is also introduced as the inverse of the attributable risk. An online calculator for NNT is referenced.