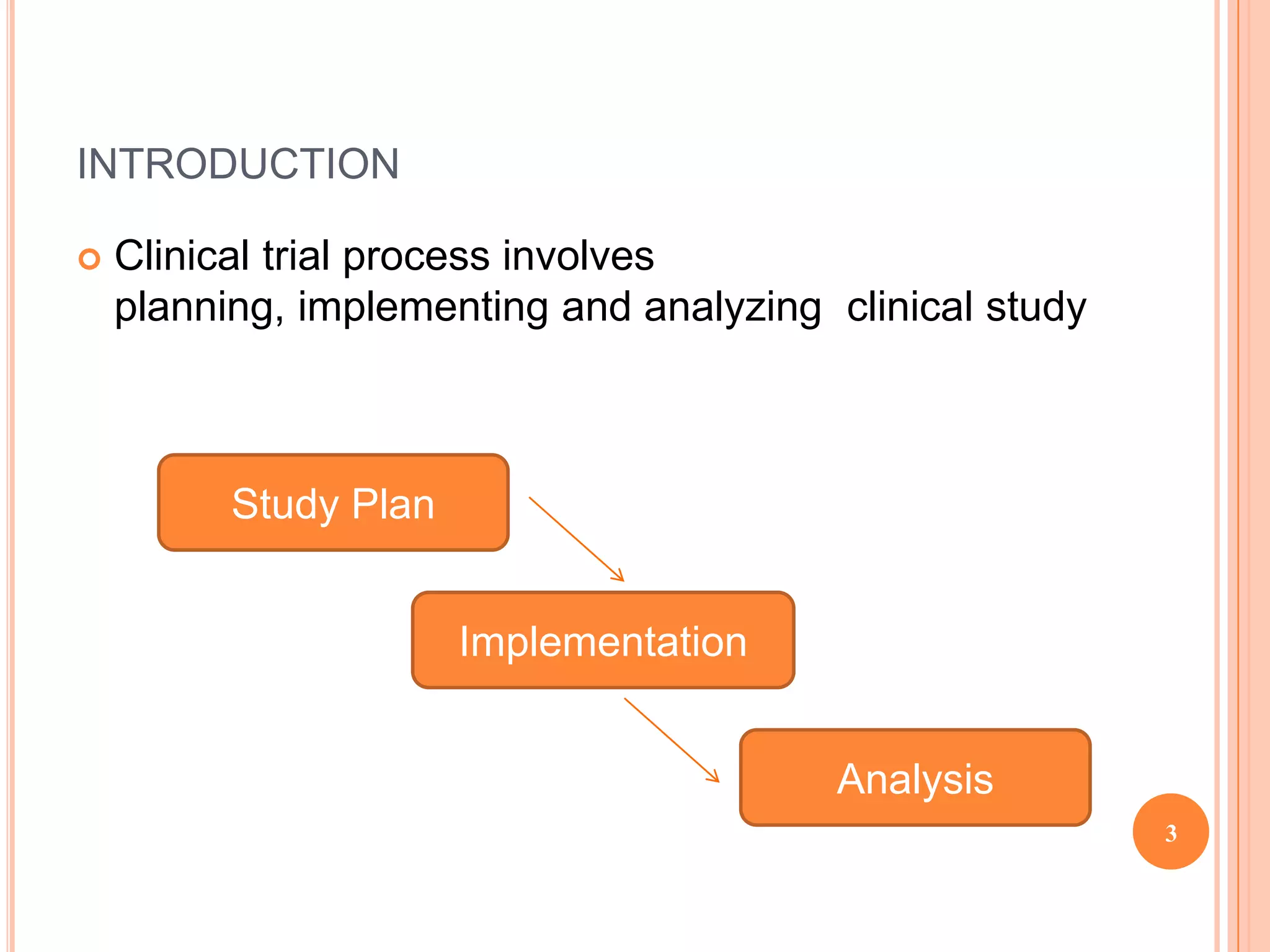
The clinical trial process involves planning, implementing, and analyzing clinical studies. The planning stage includes developing the study protocol and case report forms, designing the database, selecting study sites, and obtaining regulatory approval. During implementation, sites are activated, patients are screened and enrolled, data is collected and entered, and the database is locked. In the analysis stage, statistical analysis is conducted according to the analysis plan and clinical study reports are generated for regulatory submission. The goal is to carefully plan and implement the study to generate high quality data that can be accurately analyzed to draw clear conclusions.