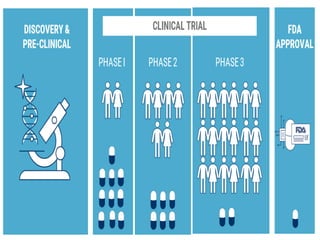
The document outlines the role of clinical pharmacy in enhancing patient care through medication history interviews, drug therapy monitoring, and participation in healthcare teams. It highlights the importance of identifying and managing drug-related problems (DRPs), providing drug and poison information services, and patient counseling. Furthermore, it emphasizes quality assurance in clinical pharmacy services and the broad scope of practice including education, research, and policy-making.