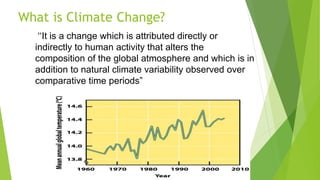
Climate change refers to alterations in the global atmosphere due to human activity, primarily through increased greenhouse gas emissions such as carbon dioxide from fossil fuel consumption. The effects include rising temperatures, sea levels, and changes in ecosystems, leading to extreme weather events and agricultural challenges. Mitigation strategies focus on reducing emissions, while adaptation involves adjusting to the environmental changes already occurring.