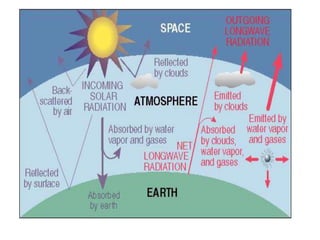
The greenhouse effect occurs naturally and helps regulate the Earth's temperature. Certain gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor, trap heat from the sun similarly to how greenhouse gases keep heat inside a greenhouse. However, increased levels of greenhouse gases from human activity are amplifying this effect and causing the planet to warm through global warming, raising sea levels and intensifying weather events like droughts and floods.