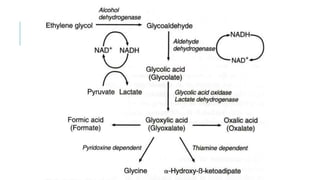
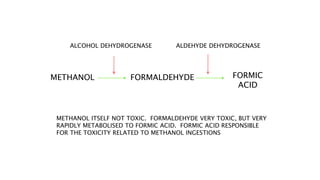
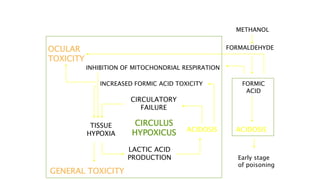
This document discusses various substances that can cause coma through exogenous intoxication, including their mechanisms of action, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. It covers ethylene glycol, which is metabolized to toxic acids responsible for metabolic acidosis and tissue injury. It also discusses barbiturates as CNS depressants, methanol which is metabolized to the toxic compound formic acid, benzodiazepines which act as GABA agonists, and opioids which act through mu, kappa, and other receptors to cause respiratory depression, analgesia, and sedation. Signs of overdose include coma, seizures, and respiratory failure. Treatment focuses on supportive care, decontamination, and use of ant