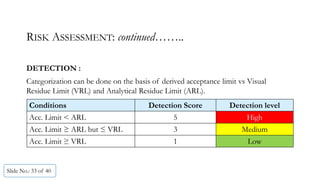
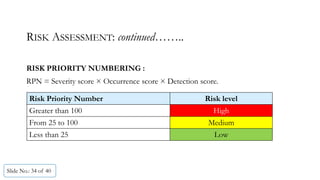
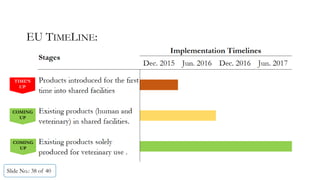
The document presents a comprehensive guide on cleaning validation focusing on a risk-integrated approach. It details principles such as the definition of cleaning validation, necessity for a risk-based approach, and methodologies for determining acceptable daily exposure limits for cleaning. Additionally, it discusses the implications of various factors influencing risk assessments and outlines a framework for evaluating product safety in shared manufacturing environments.