This document provides information on classification systems for organisms, including:
- Originally all life was grouped into two kingdoms: plants and animals.
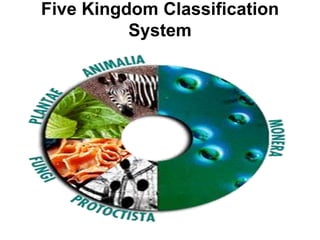
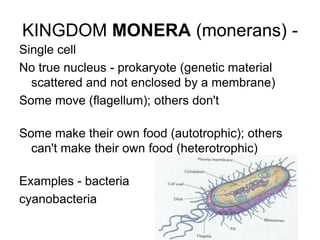
- This was later expanded to five kingdoms: Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia, and Monera.
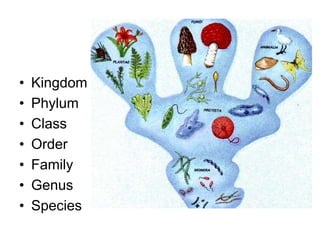
- Kingdoms are further divided into categories like phyla, classes, orders, etc.
- Details are given on the characteristics of each kingdom and examples of phyla in the animal kingdom like porifera, cnidaria, chordata etc.