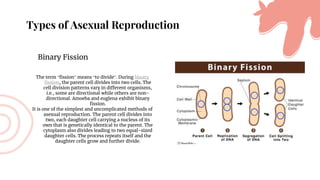
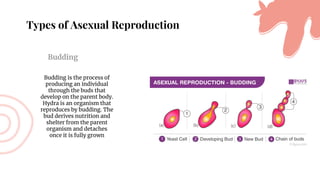
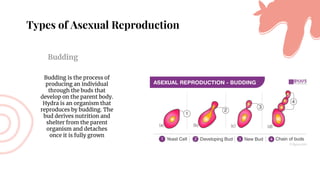
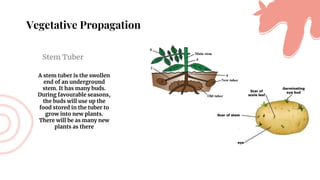
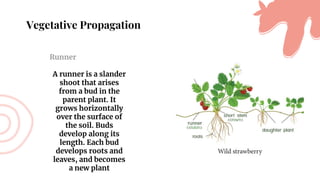
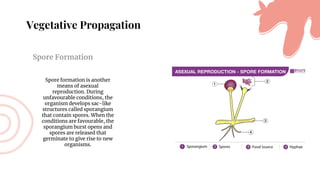
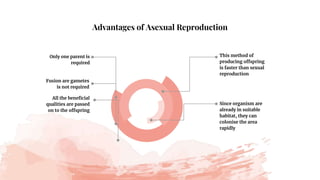
This document discusses asexual reproduction in plants. It begins by defining asexual reproduction as reproduction that requires only a single parent and does not involve the fusion of gametes. It then discusses various types of asexual reproduction including binary fission, fragmentation, budding, vegetative propagation, and spore formation. The key advantages of asexual reproduction are that it only requires one parent and offspring are produced more quickly than sexual reproduction, allowing for rapid colonization. However, the main disadvantage is lack of genetic diversity, making the offspring and entire species more vulnerable to environmental changes.