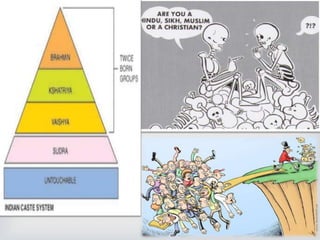
This document discusses equality and inequality in India. It covers types of inequality like gender, income, education, caste/religion. It discusses government efforts to promote equality like constitutional rights and affirmative action. However, inequality still persists in many forms like gender-based abortion, increasing rich-poor gap and lack of safety for women. While progress has been made in recent years through education, reforms and development programs, achieving true equality remains a challenge and work still needs to be done.