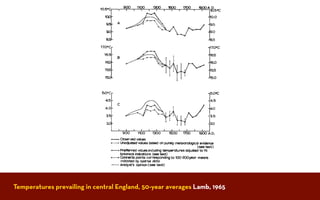
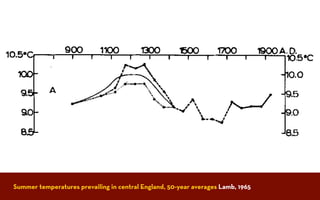
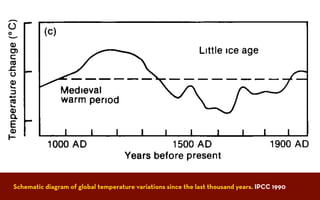
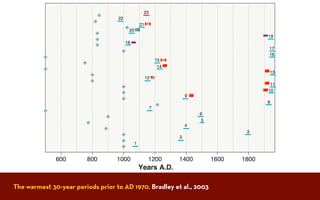
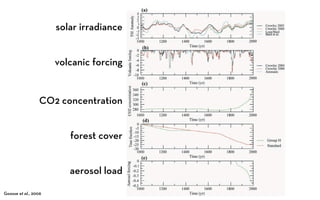
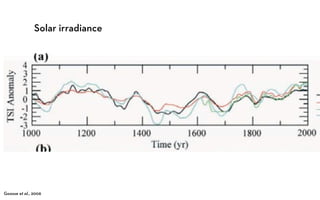
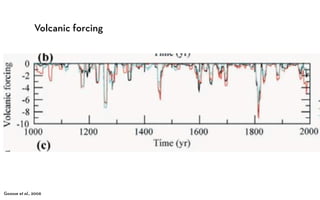
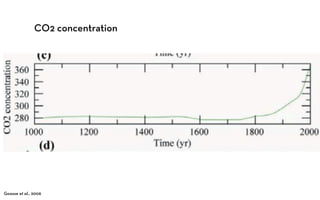
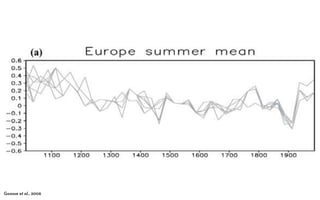
The document discusses the Medieval Warm Period between approximately 900-1300 AD. It provides evidence from historical records of warmer conditions in parts of the world during this period compared to later centuries. Climate data from central England and temperatures in Europe are discussed. While some regions like China were cooler, other areas like South Japan and Western Europe experienced warmer temperatures during this time compared to after 1300 AD, known as the Medieval Climate Optimum. There is debate around the extent and causes of warming, with more evidence needed to fully understand natural variability compared to potential human influences on climate.















![By November 3
[Tentative] list of 10 articles related to
your region and time period.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/megadroughtii-101026200857-phpapp02/85/Class-7-Megadroughts-II-25-320.jpg)