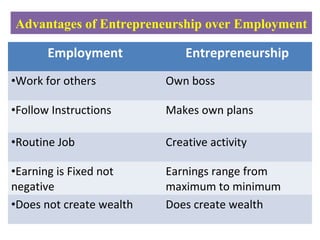
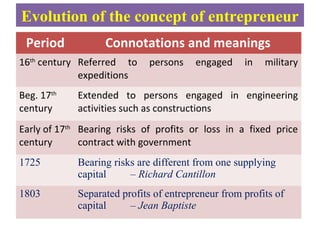
The document traces the evolution of the concept of entrepreneurship from the 16th century to present. It began referring to those engaged in military expeditions, then was extended to engineering activities like construction. In the early 17th century, it took on the meaning of bearing risks of profits or losses in contracts. Later thinkers further refined the definition to separate entrepreneur profits from capital profits and identify entrepreneurs as innovators who develop new technologies and maximize opportunities. Modern definitions characterize entrepreneurs as applying knowledge and skills to create new businesses or diversify existing ones in order to pursue growth, generate wealth and employment, and create social good.