1. Solidification of metals occurs through nucleation and growth processes. Nucleation can be homogeneous (within the bulk liquid) or heterogeneous (on foreign particles). Heterogeneous nucleation is more common.
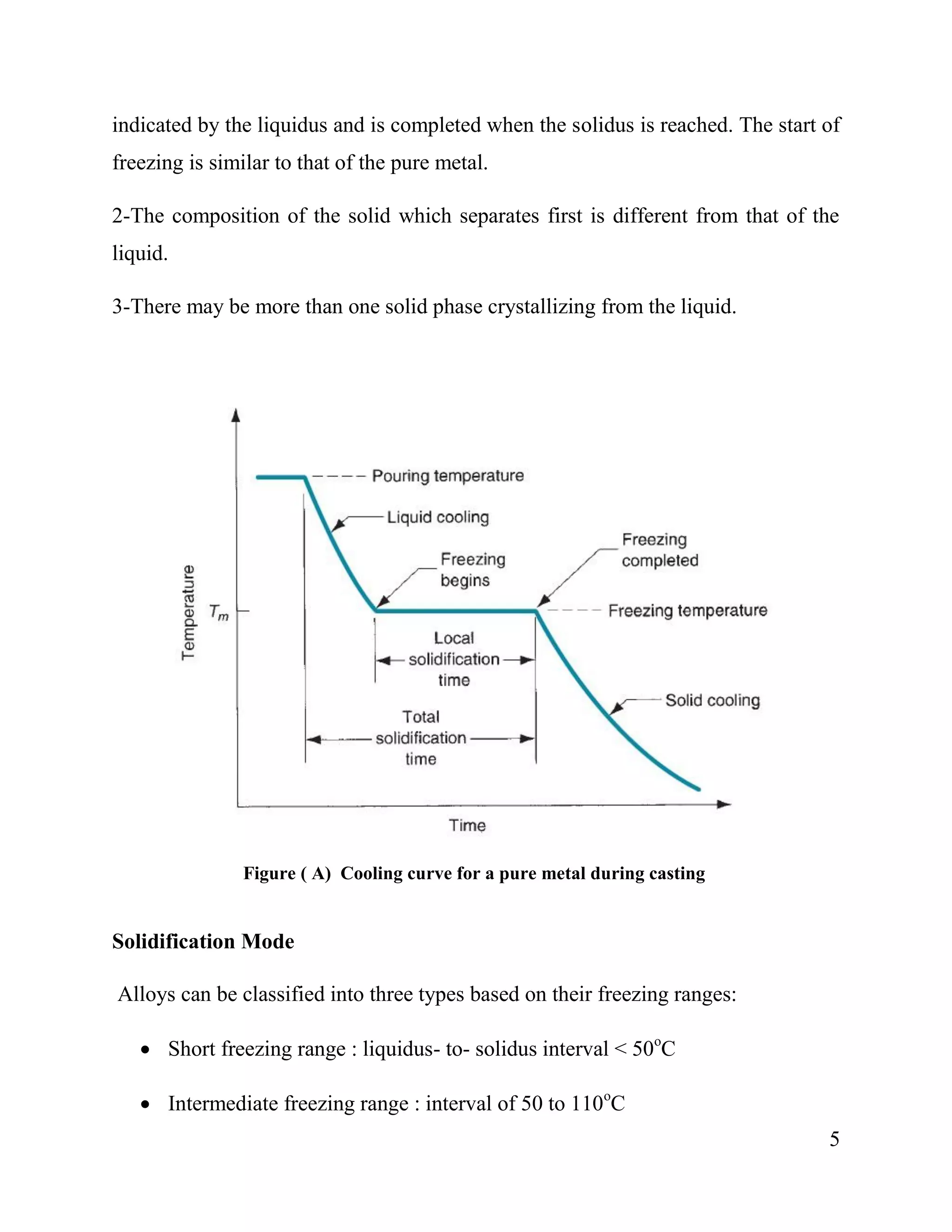
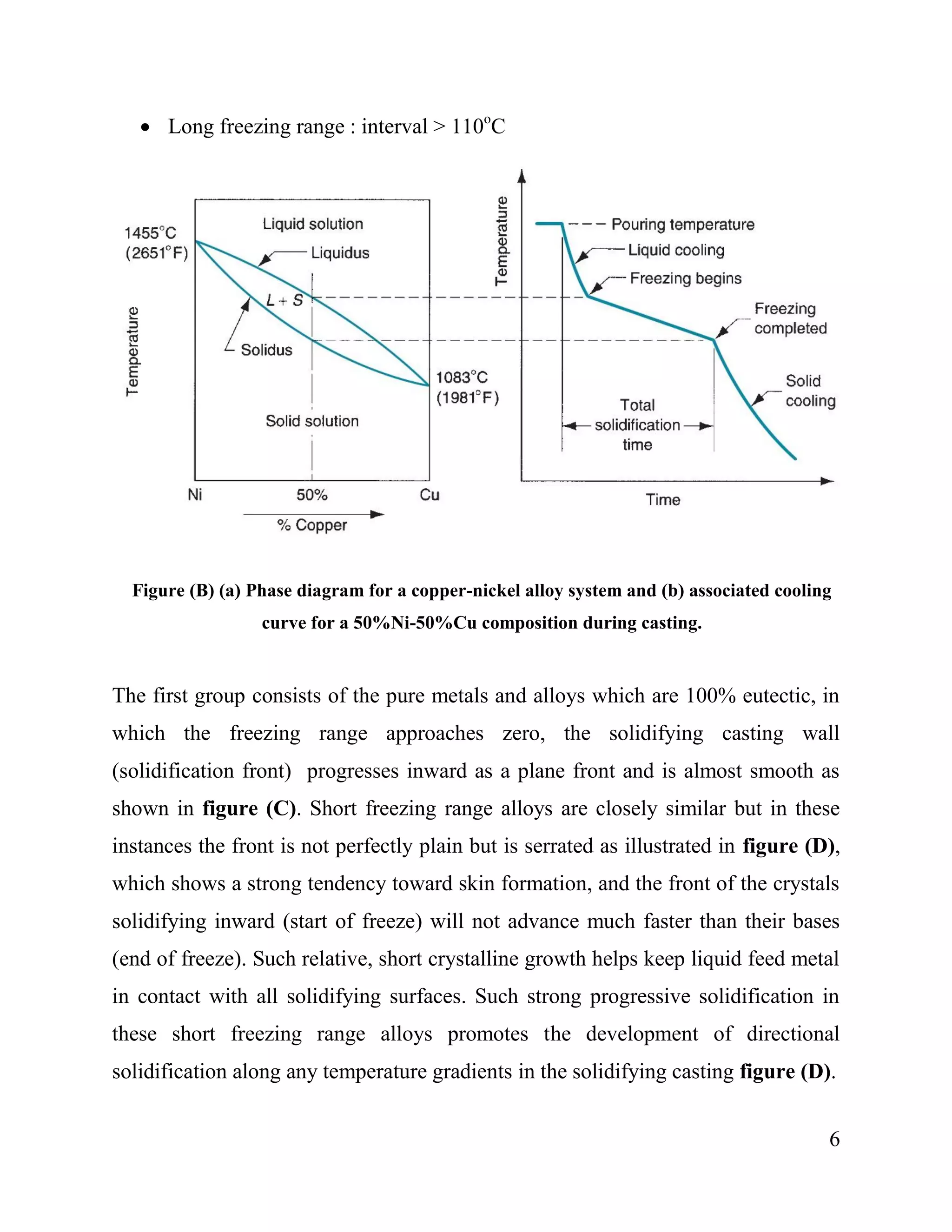
2. Pure metals solidify at a single, constant temperature, while alloys solidify over a temperature range from the liquidus to solidus temperatures. The first crystals to form in an alloy have a different composition than the remaining liquid.
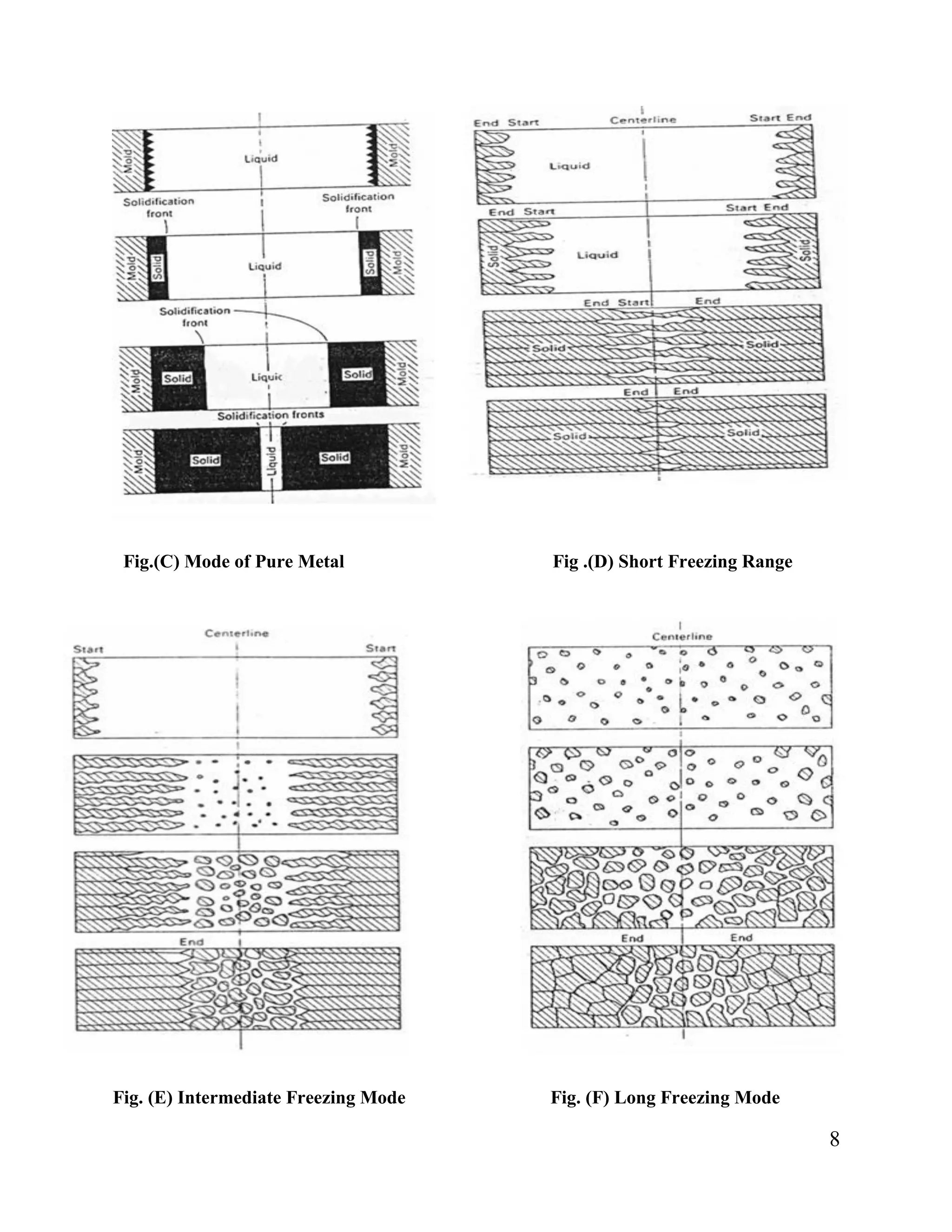
3. Alloys are classified by their freezing range into short (<=50°C), intermediate (50-110°C) or long (>110°C) freezing ranges. Short and intermediate ranges solidify with a planar or serrated front, while long ranges