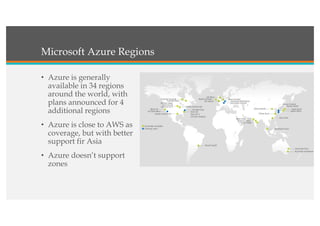
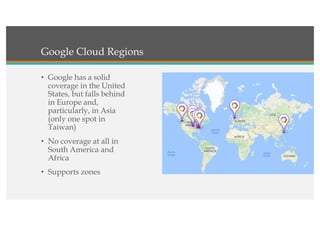
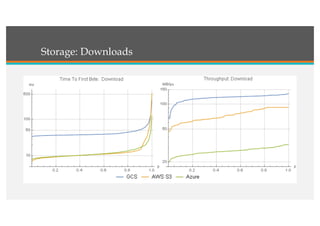
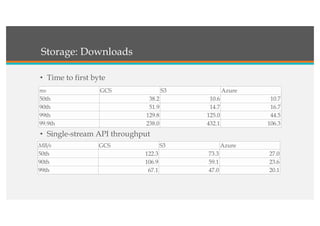
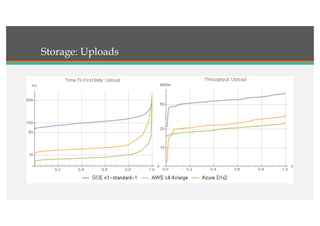
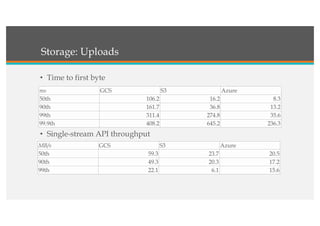
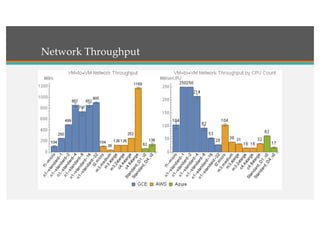
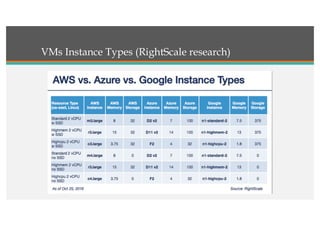
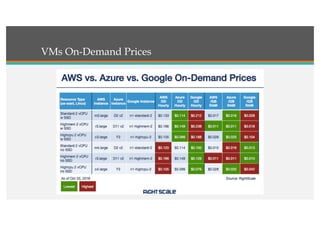
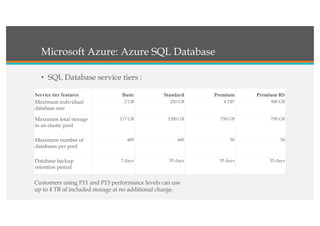
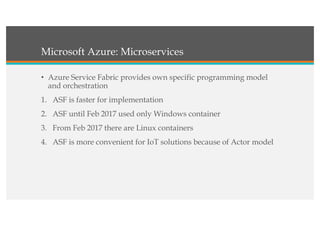
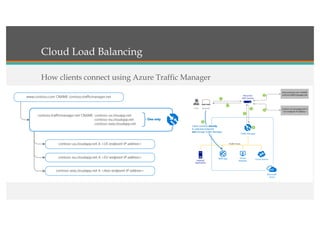
This document compares Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure on various features. It discusses their pricing models, infrastructure as a service and platform as a service capabilities. Some key findings are that Azure has better coverage in Asia while Google Cloud has better coverage in the US. AWS leads the cloud market currently. The document also analyzes storage performance, virtual machine pricing and types, database offerings, microservices support, load balancing options and example use cases for each provider.