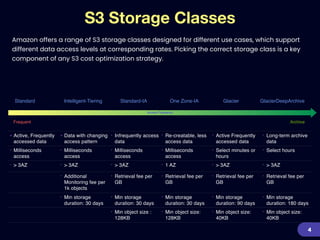
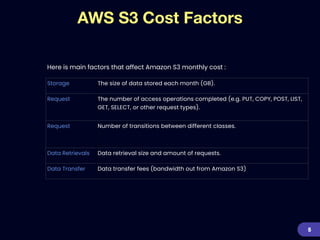
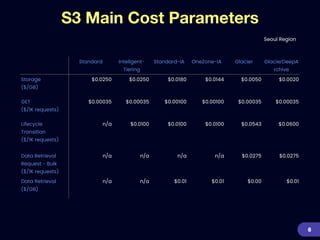
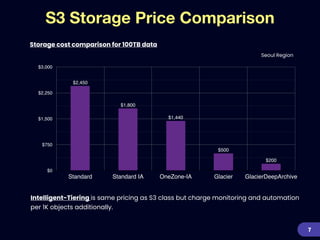
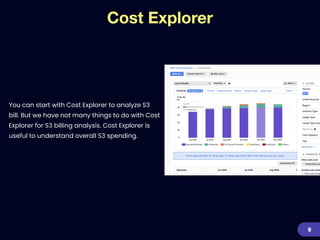
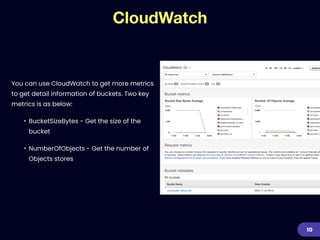
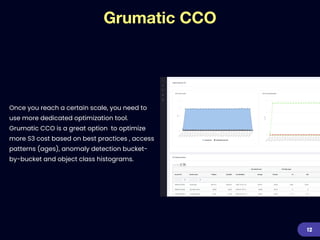
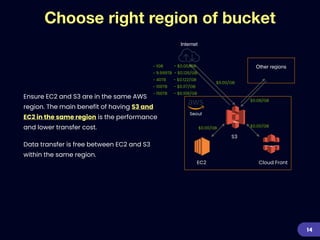
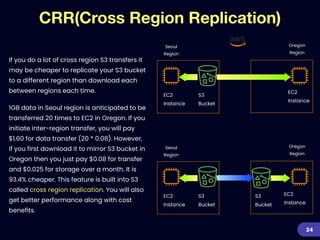
This document provides an overview of strategies for optimizing costs with Amazon S3 storage. It discusses S3 pricing fundamentals, analyzing S3 bills, and provides a guide to optimization techniques. The key techniques include choosing the right storage class based on access patterns, using lifecycle policies to transition objects, removing unused objects, optimizing data formats, and replicating data across regions. Analyzing object storage usage and getting actionable recommendations is suggested to effectively optimize S3 costs at scale.