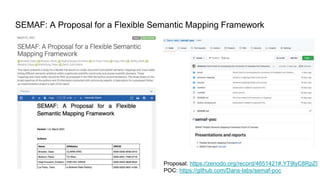
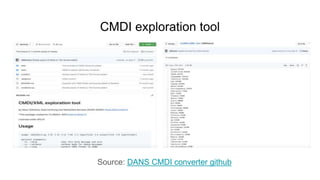
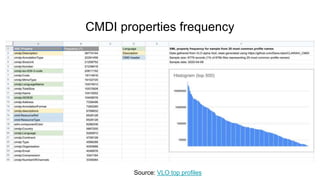
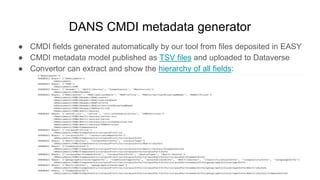
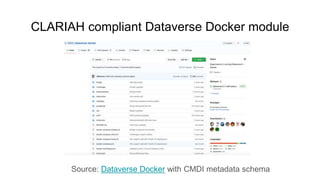
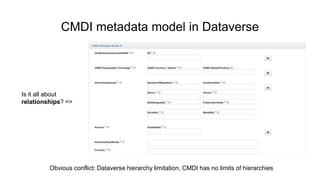
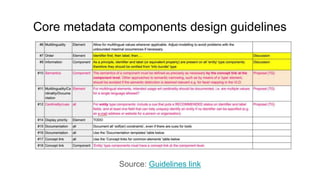
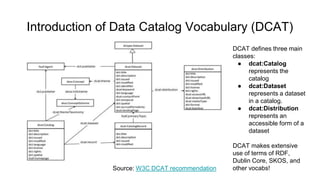
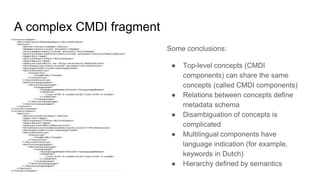
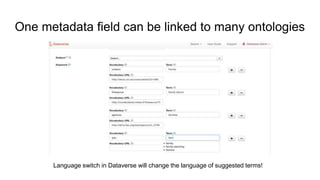
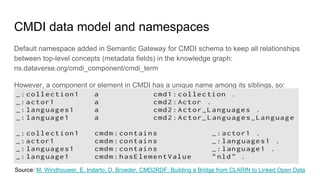
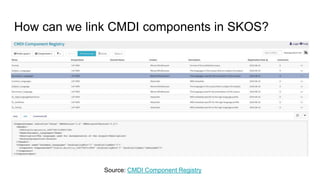
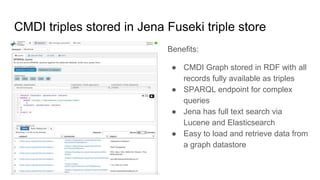
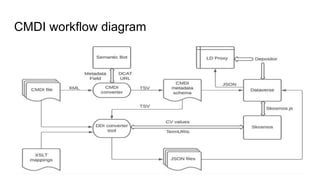
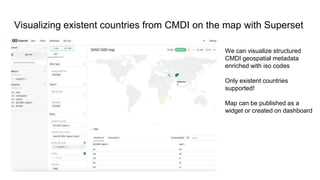
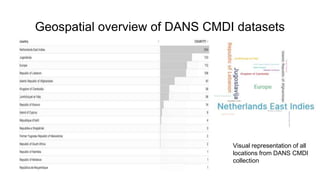
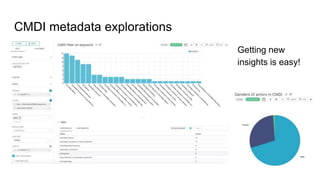
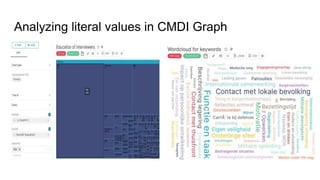
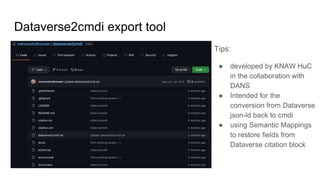
The document outlines the goals and challenges of developing flexible metadata schemes for research data repositories, particularly focusing on CMDI (Common Metadata Infrastructure) for CLARIN centers. It details the structure and integration of metadata components, the implementation of FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) controlled vocabularies, and the relationship between CMDI and Dataverse platforms. Additionally, it highlights the use of external APIs and semantic interoperability to enhance metadata management and visualization tools for research datasets.