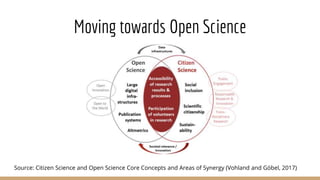
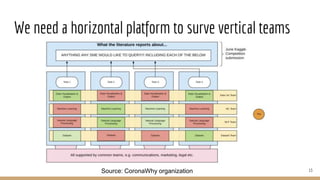
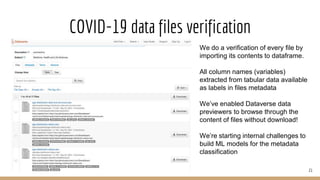
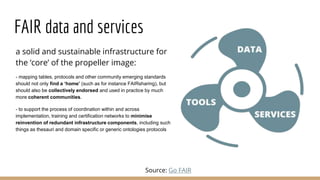
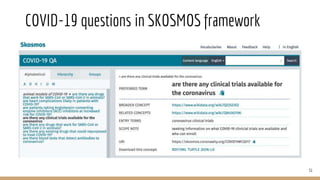
The document presents the use of artificial intelligence and collaborative platforms to enhance research on COVID-19, particularly through the coronawhy initiative, which aims to improve data sharing and accessibility. It highlights various tasks undertaken by the coronawhy community, the role of the COVID-19 Open Research Dataset (CORD-19), and the need for effective interoperability among diverse data sources. The discussion emphasizes the importance of fair data principles, the integration of AI in research processes, and the establishment of a common data infrastructure to support ongoing research and collaboration.