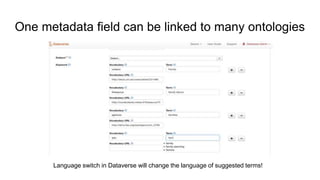
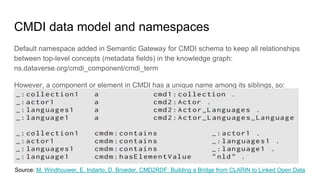
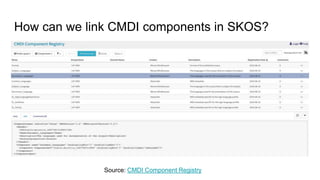
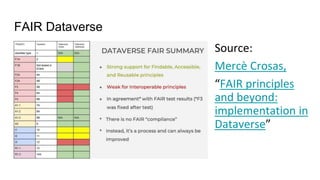
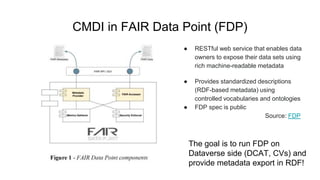
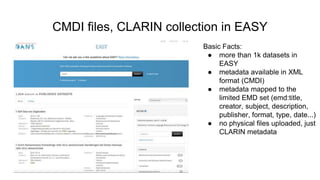
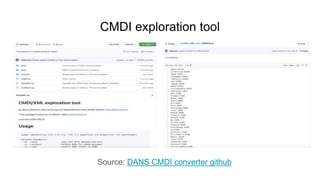
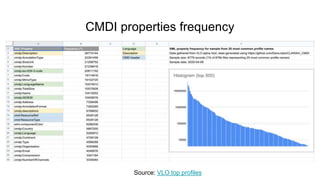
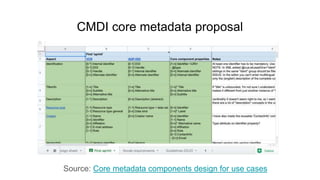
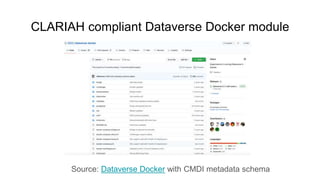
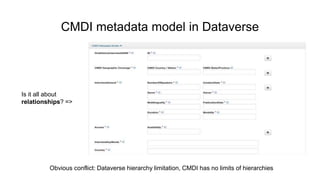
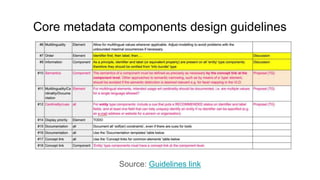
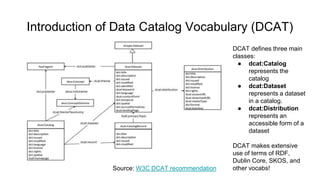
The document outlines the objectives and implementation of CMDI (Common Metadata Infrastructure) support within Dataverse for various CLARIN centers, focusing on improving metadata quality and interoperability with external vocabularies. It discusses the structure of CMDI metadata components, including the integration of controlled vocabularies and the capabilities of a semantic gateway to enhance accessibility and multilingual support. Additionally, it highlights the plans for metadata harvesting and the necessity of adhering to FAIR principles in data management.






![What is semantics?
Semantics (from Ancient Greek: σημαντικός sēmantikós, "significant")[a][1] is the study of meaning. The term can be used to
refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines including linguistics, philosophy, and computer science.
Linguistics
In linguistics, semantics is the subfield that studies meaning. Semantics can address meaning at the levels of words,
phrases, sentences, or larger units of discourse. One of the crucial questions which unites different approaches to linguistic
semantics is that of the relationship between form and meaning.[2]
Computer science
In computer science, the term semantics refers to the meaning of language constructs, as opposed to their form (syntax).
According to Euzenat, semantics "provides the rules for interpreting the syntax which do not provide the meaning directly
but constrains the possible interpretations of what is declared."[14]
(from Wikipedia)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmdisupportindataverseclarinpresentation-201202150205/85/CLARIN-CMDI-support-in-Dataverse-19-320.jpg)